The Castle Studies Trust is delighted to announce the award of five grants, totalling a record amount of £42,000, to a wide range of projects with different types of research. The amount means that since our foundation we will have given over £300,000 to castle research projects – a landmark to celebrate.
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
The five projects we will be funding are:
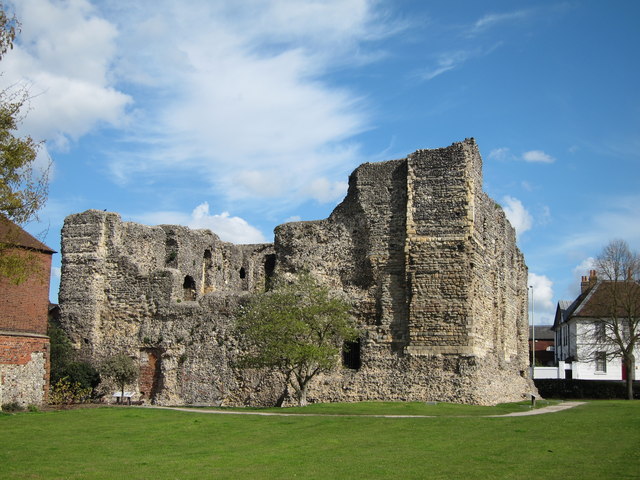

Canterbury, Kent: To create an interactive digital model of the castle’s keep. The keep is one of the largest surviving from early Norman England dating to the late eleventh / early twelfth century. Now much ruined and inaccessible to visitors due to instability, the project will use the findings of previous archaeological research to create an interactive model. Work will start in March and be completed within ten months.
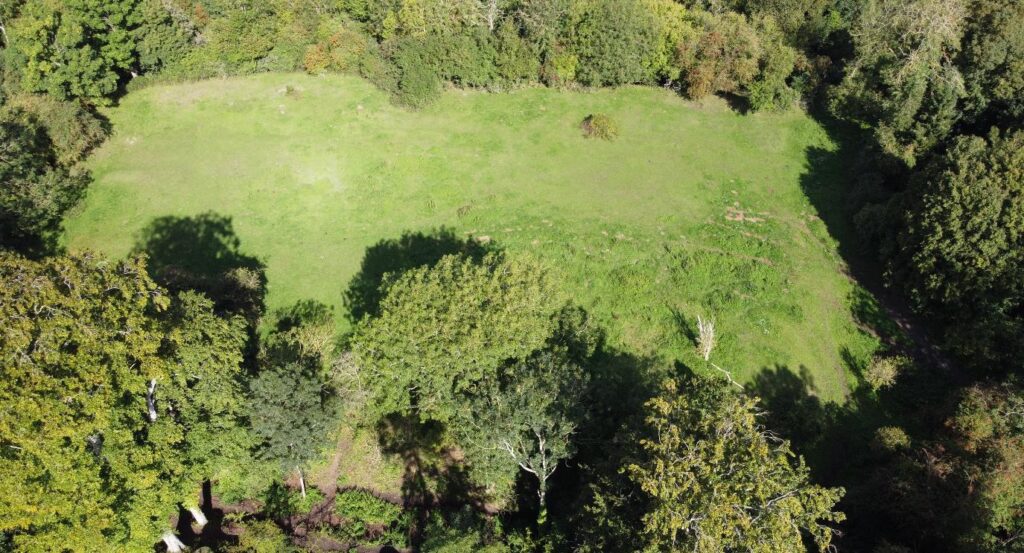

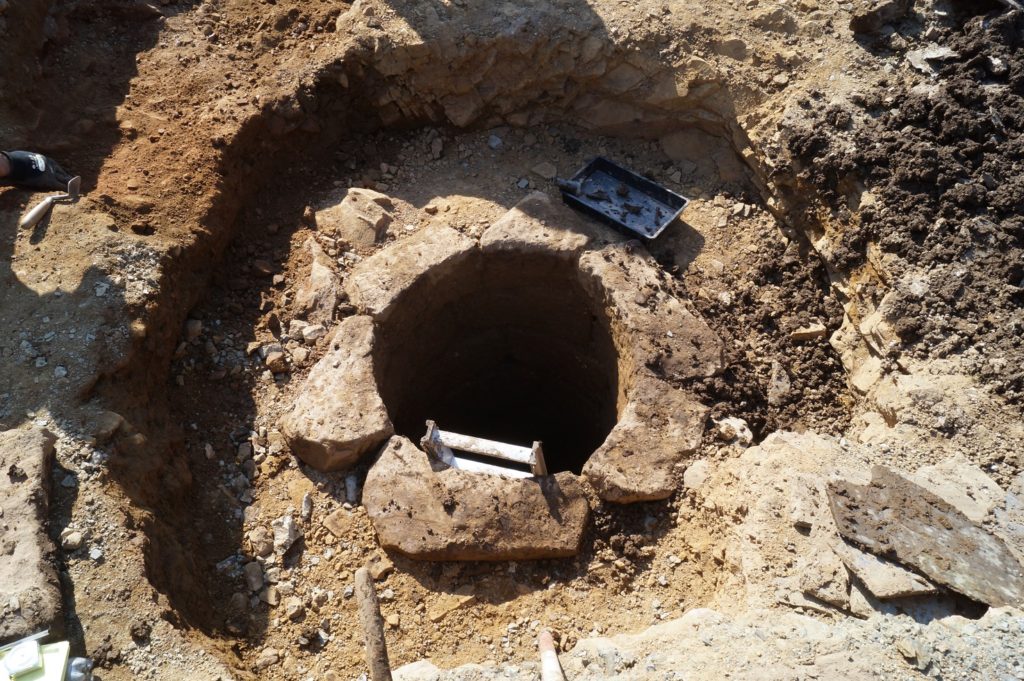
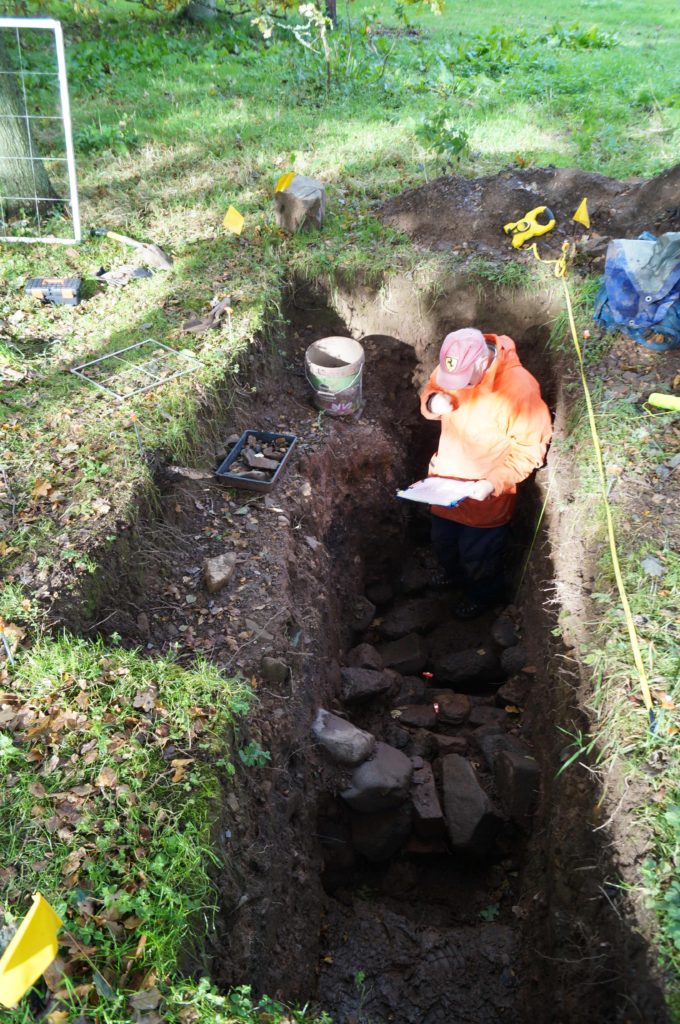
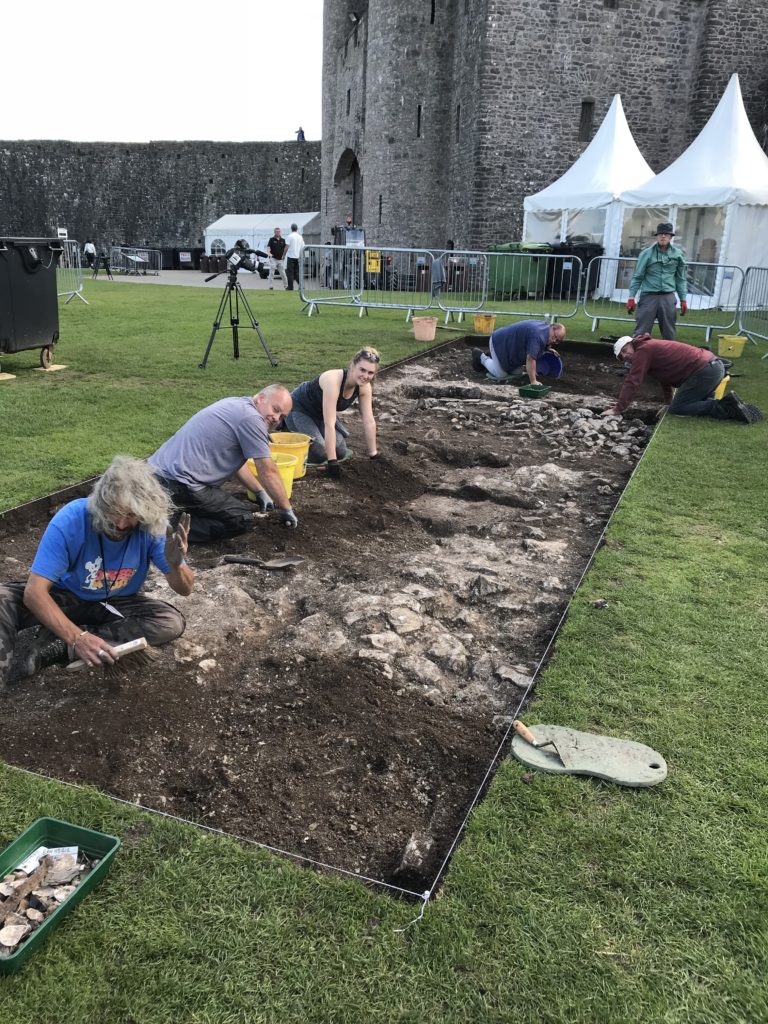
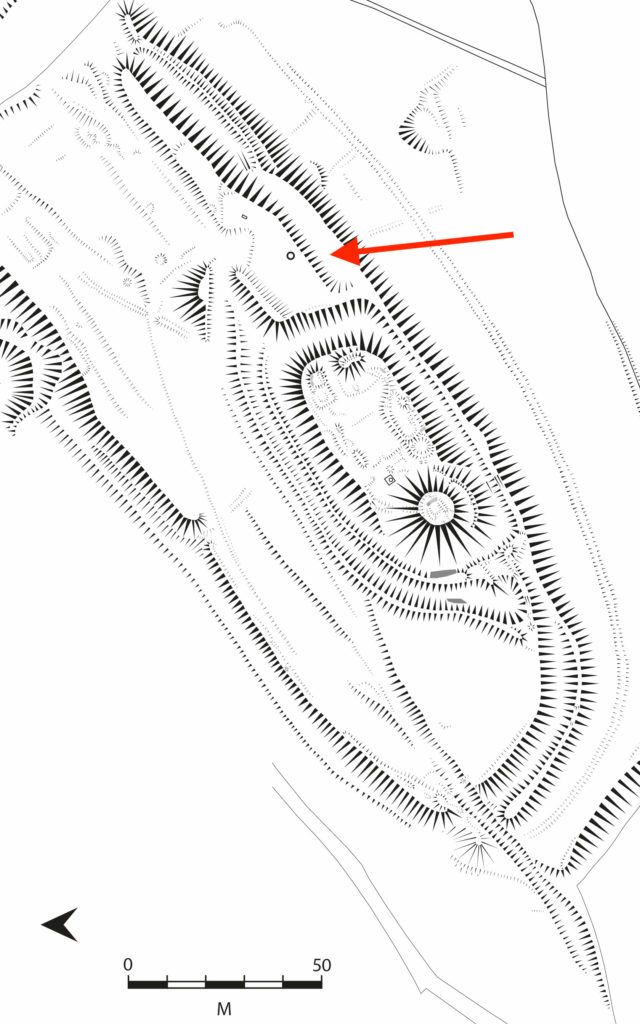
Clavering, Essex: To fund an excavation to help understand the development of the site which was occupied for over 600 years and which could be one of the very few pre-conquest castles in the UK. The excavation will build on the extensive survey work carried out by the local group of the site. They are planning to do the excavations in June.
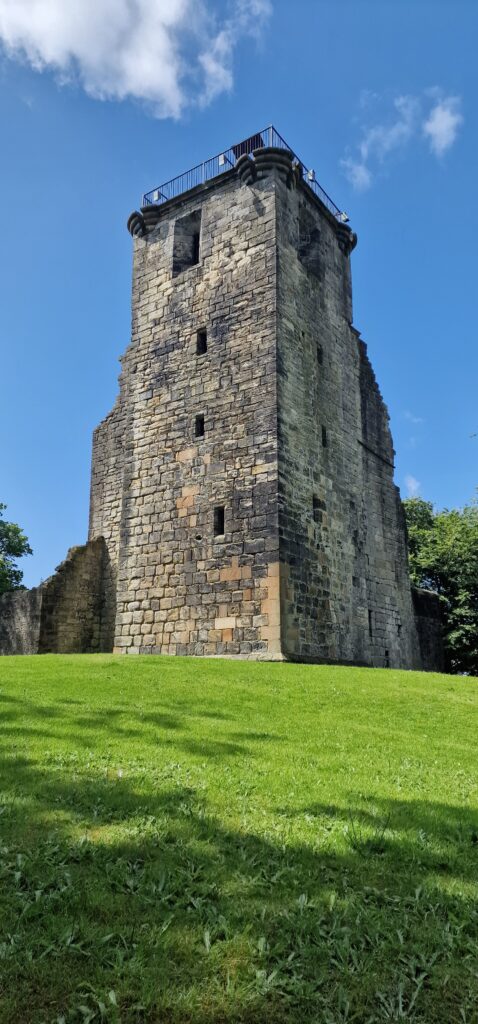

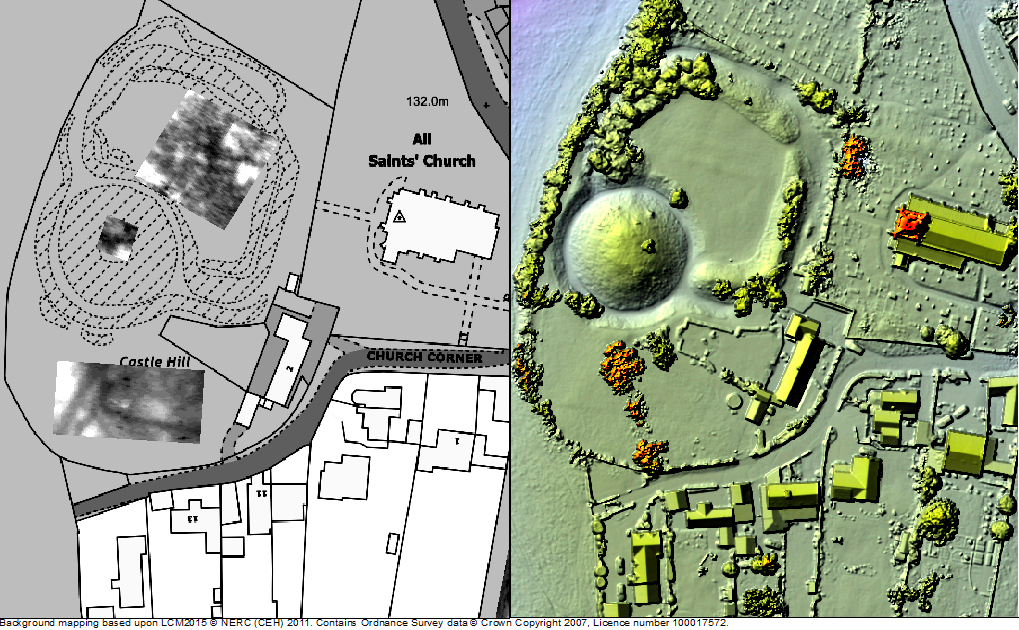
Crookston, Glasgow: A community-led geophysical survey, using multiple techniques, through which the Friends of Crookston Castle in conjunction with HES hope to learn more about Glasgow’s only castle. While the standing remains are believed to date from the early fifteenth century, it is believed that the castle dates back to the twelfth century. The group hopes to discover evidence of that earlier history and whether it was based on an earlier Iron Age hillfort. They plan to do the survey in early August.
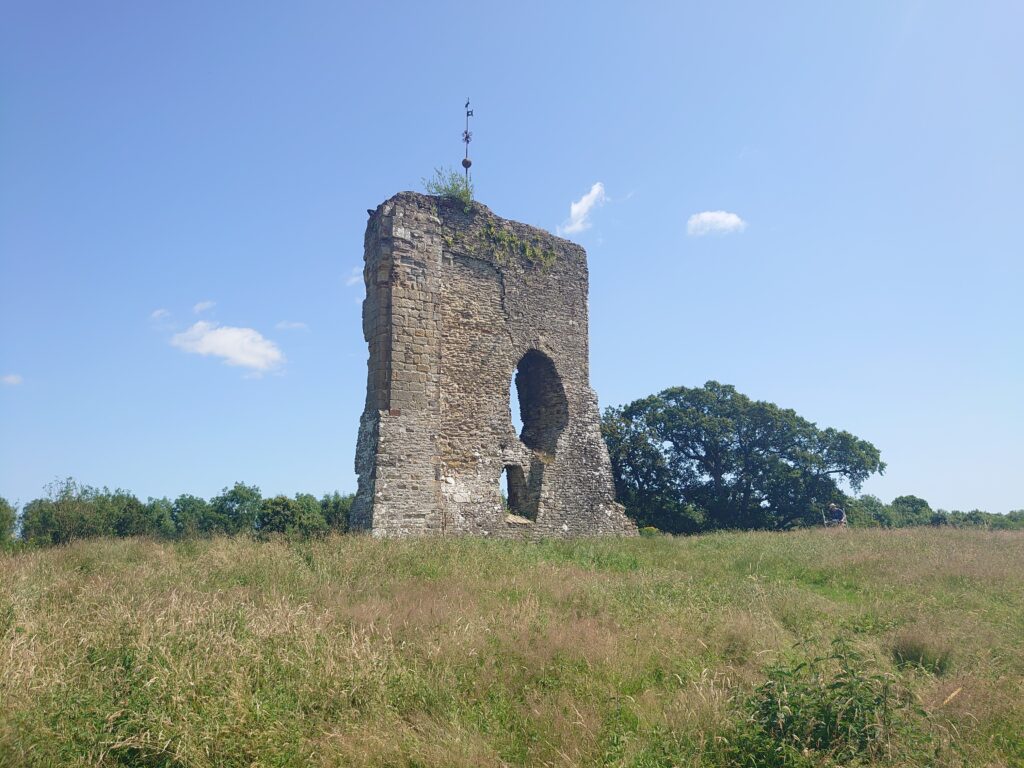

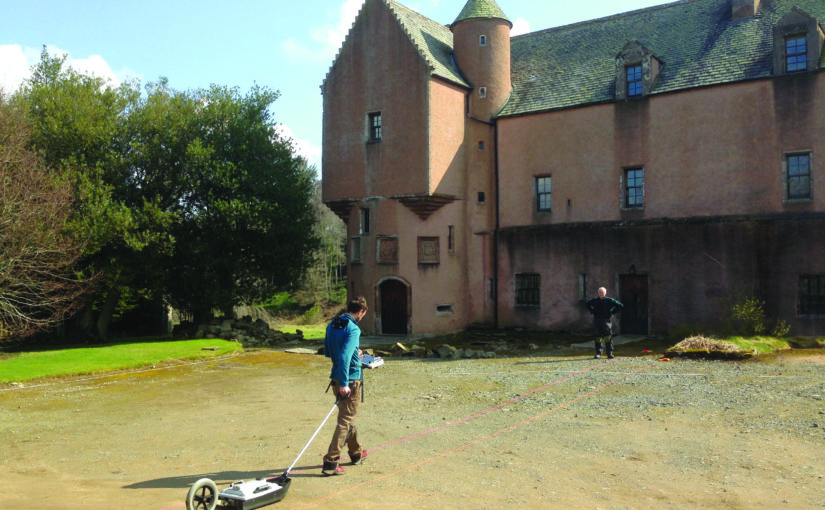
Knepp, West Sussex: An excavation building on a geophysical survey to better understand the site’s development and its relationship to the local area of this important baronial centre thought to be built by the de Braose family. The first documentary evidence is from 1210 when it was under royal control, documenting repairs, while the geophysical survey shows activity that pre-dates the extant stone tower. Excavations are planned for late July/ early August 2025.

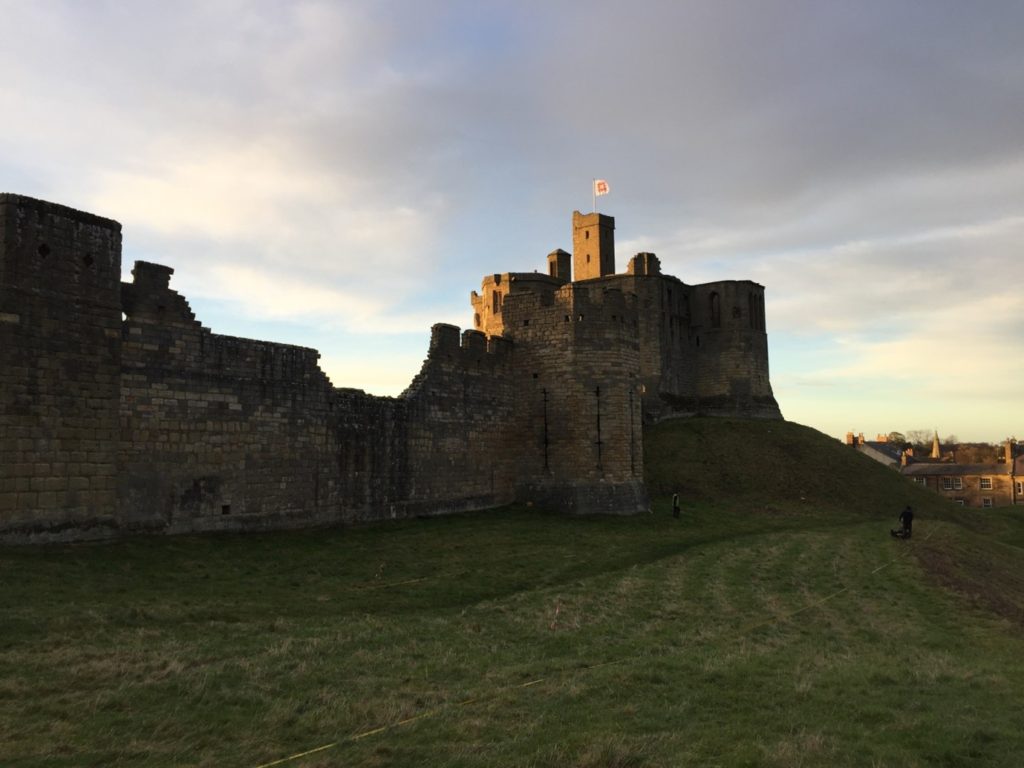
Transcription and translation of C17 Dutch Engineer’s Survey of English castles and fortifications: A joint project between Dutch academic Dr Esther van Raamsdonk and English Heritage to transcribe and translate part of an early seventeenth-century manuscript of a Dutch surveyor’s examination of castles and forts in England. The sample covers five of the 22 castles and fortifications in the document, which is called SP 9/99, held by the National Archives in Kew. The sample will include Dover, Walmer and Deal. The document is filled with detailed drawings and maps of these fortifications with often lengthy descriptions of their condition. Esther has already started work on it.