Project leads, Drs Sarah Jane Gibbon and Dan Lee reveal the results of the geophysical survey part of their project on The Wirk funded by the Castle Studies Trust.
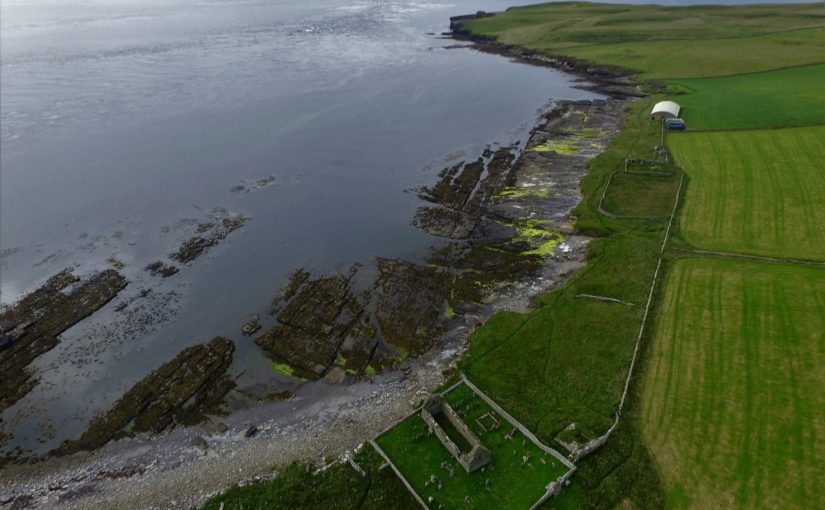
Thanks to a grant from the Castle Studies Trust, ateam from the Orkney Research Centre for Archaeology undertook geophysical survey at The Wirk, Westside, on the island of Rousay, Orkney in September, despite the challenges. Long grass was cleared from the site and a grid was established to the north, east and west of the stone-built tower. Two techniques were used: magnetometer survey (good for identifying magnetically enhanced material from burning and settlement activity) and earth resistance (good for locating walls and structures).
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
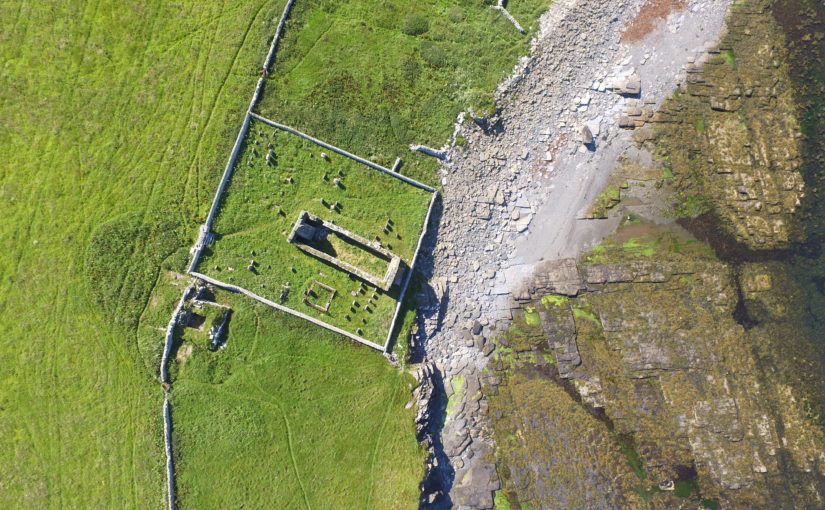
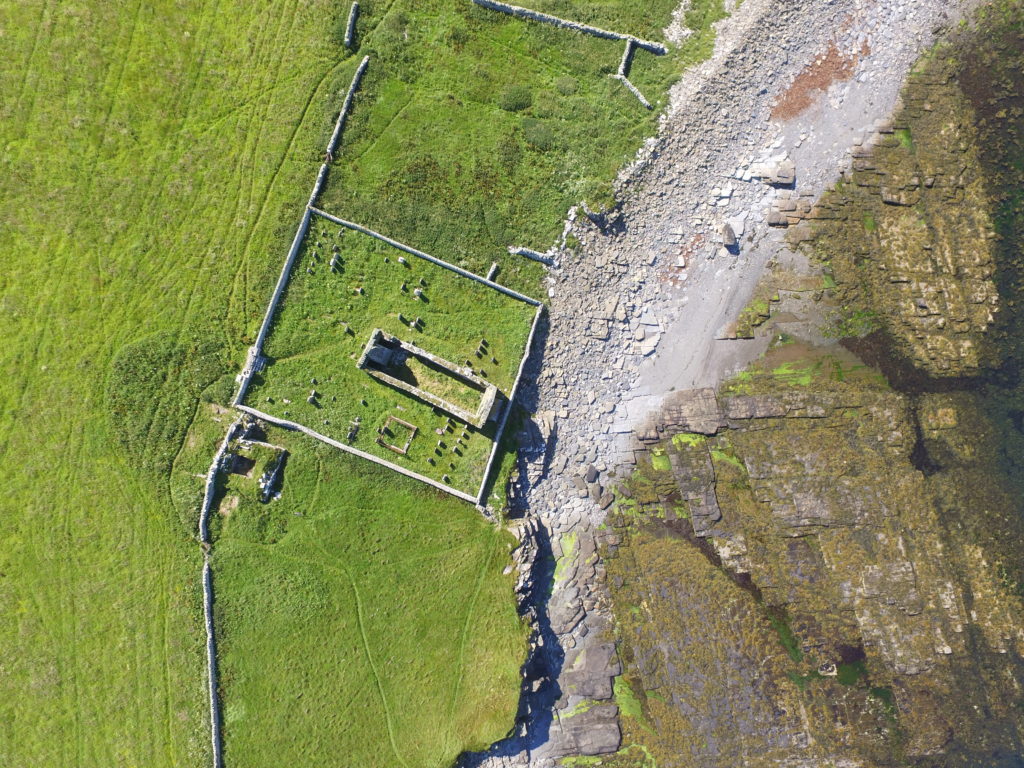
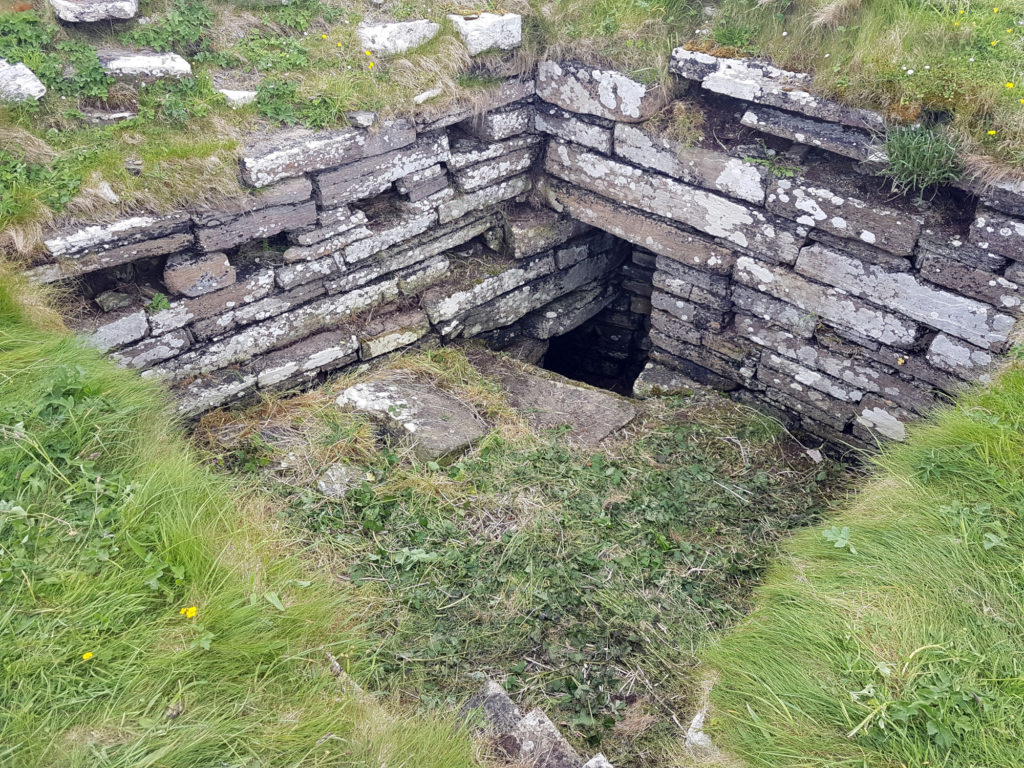
The aim is to better understand the nature and date of the tower which has variously been interpreted as a 12th century Norse Castle, a hall-house tower, a defensive church tower and a 16th century tower and range. Previous excavations by J. Storer Clouston in the 1920s cleared the stone tower and exposed a large range to the east, although phasing of the buildings remains unclear. The tower was left exposed but the area to the east was backfilled. A scale plan was made but recording and description of the built remains was minimal.
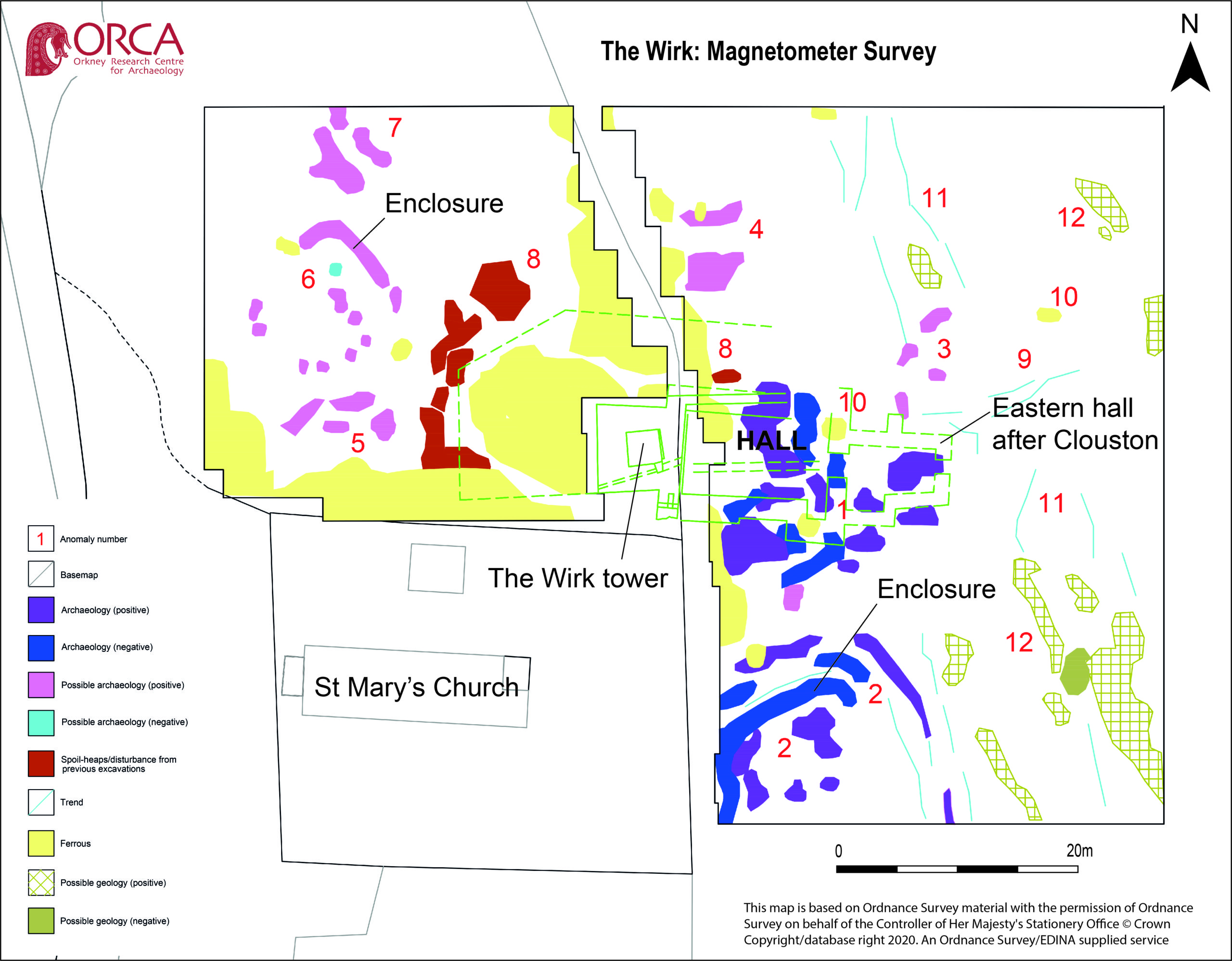
High-resolution magnetometer survey and targeted high-resolution earth resistance survey was undertaken across the site in order to characterise the buried structures, put the tower and hall in context and inform trench location. Clear anomalies were identified in both surveys at the site of the hall, with potential wall lines (high resistance) matching the main part of the building in Clouston’s plan to the east of the tower. This suggests that wall footings are likely to survive just below the ground surface. Other high resistance anomalies to the south of the hall could indicate the presence of additional structures. Results from the magnetometer survey showed strong positive and negative anomalies within the footprint of the hall and confirmed the presence of a possible enclosure to the south. A curvilinear positive anomaly to the north-west of the tower, beyond the apron, could indicate the presence of another small enclosure.
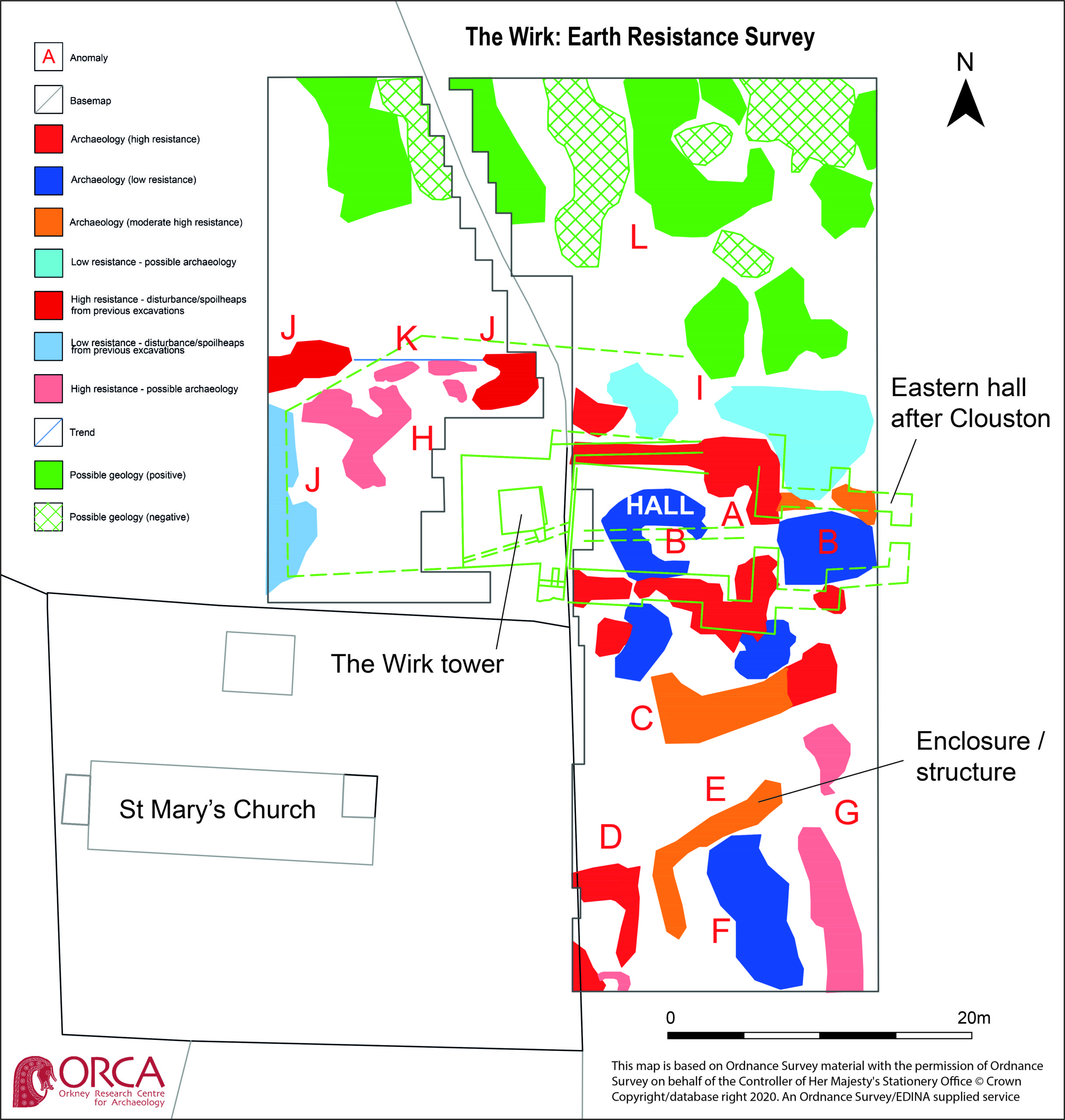
Overall, the geophysical survey has demonstrated that the footings of the hall survive to the east of the tower, accompanied by newly discovered enclosures with possible structural elements to the south and north-west. The extent of the site appears to extend beyond the visible remains with anomalies continuing into the kirkyard.
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
Featured image copyright of Bobby Friel @TakeTheHighView
ORCA have had to postpone the evaluation excavation until next year, but the prospects are looking good to expose some of the hall.




