Project lead, Dr Richard Tipping, looks back at the second week of fieldwork he and Dr Eileen Tisdall are undertaking to try establish whether climate change did impact the re-positioning of Caerlaverock Castle.
Home again – after one of the most torrid week’s fieldwork I can recall: whilst Northern Ireland had the extreme weather warnings just to the east, Dumfries had day-time temperatures exceeding 26⁰C all week. And you’ll recall that I was inside a wood, where breezes never penetrate.
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
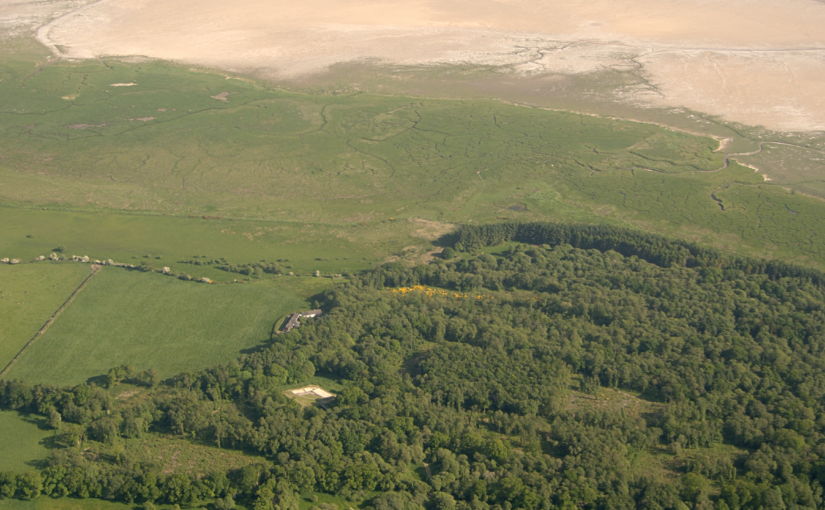
At Caerlaverock on the Solway coast, we are trying to work out the natural and human impact of huge medieval storm surges on the 13th century old castle. Last time I was looking at how the moat, and possibly the castle itself, was inundated with seawater and mud driven shoreward by storms. This week I focused on the coastline itself, away from the castle. Before the storms hit, the old castle was on the coast: it had a harbour. You can still walk along the degraded cliff to the west of the castle and imagine the seascape. After the storms, the coast lay some 250 metres south of the castle. A series of large gravel ridges, tens of metres wide, grew southward, beautifully revealed in LiDAR images that peel away the nearly impenetrable woodland.
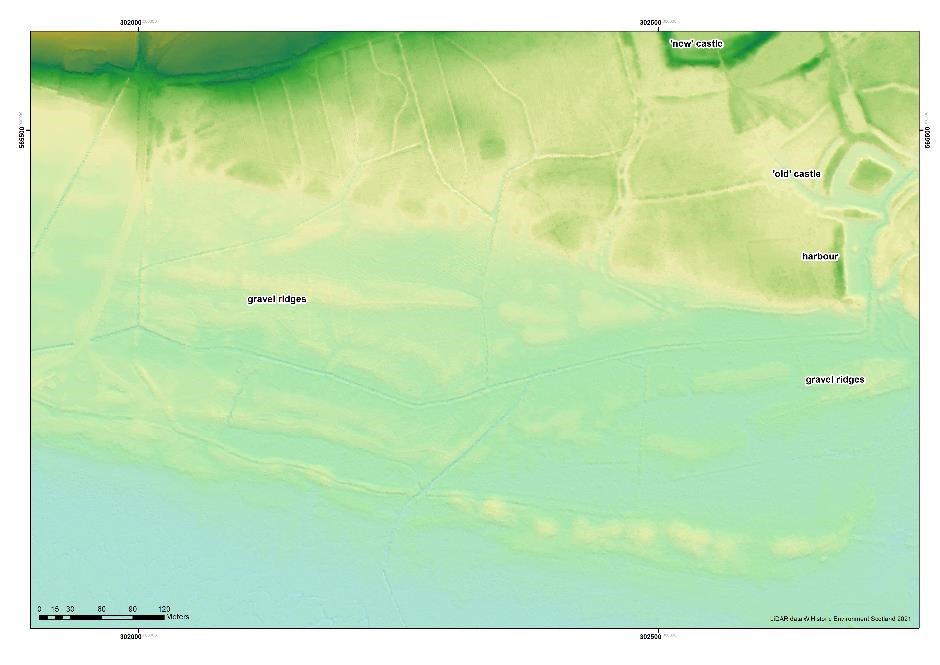
Each of these ridges created shallow basins protected from tides. The harbour became pointless as a result. But all we knew from earlier work was that the youngest basin was formed around AD1400. How old were the earlier ones? Could we find sediment dateable by radiocarbon?
The fieldwork, I knew, would be hard. I’d looked for dateable sediment before, simply by coring the sediments in the basins, and found only one site; and now there was the woodland to contend with. All you can do is remain patient and optimistic: unglamorous, muddy and unspectacular work. The woodland meant that some basins couldn’t now be found, others where I couldn’t core systematically, and still others where systematic coring failed to find anything to excite. But I think we can date three of the eight basins and, usefully, these include the earliest basin and the basin that blocked the harbour. Stay tuned.
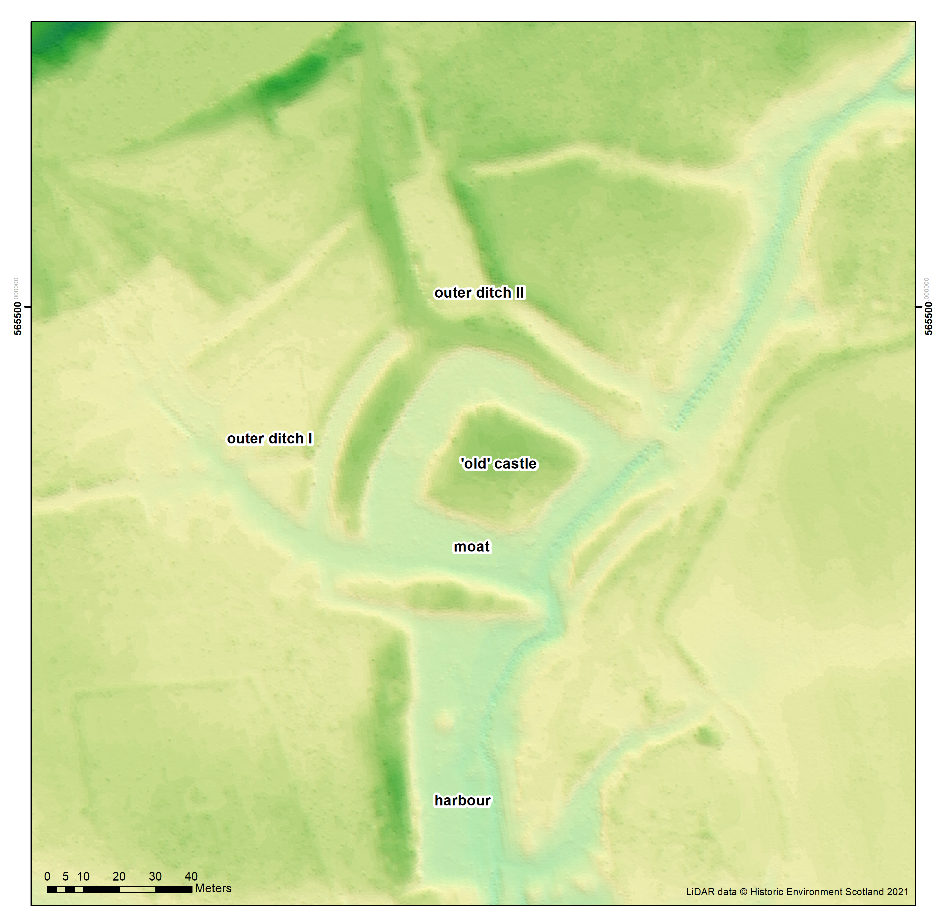
But it was the ditches around the old castle that were the highlight of a difficult week. Sense was made of the moat. The builders formed one of the four moat sides from an existing stream channel: the moat here is a lot deeper because of this. But then the castle mound was not made parallel with this moat side. It does seem to be a very slap-dash construction. The attempted buttressing of the castle by stonework in the moat is shown here.
And we can now show that the mud of the storm surges penetrated beyond the castle, not by a great distance but enough that the old castle would have been surrounded in these extreme events, laid siege by nature while the younger new castle was laid siege by Edward I and the English in AD1300.
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
Feature image courtesy of Historic Environment Scotland
