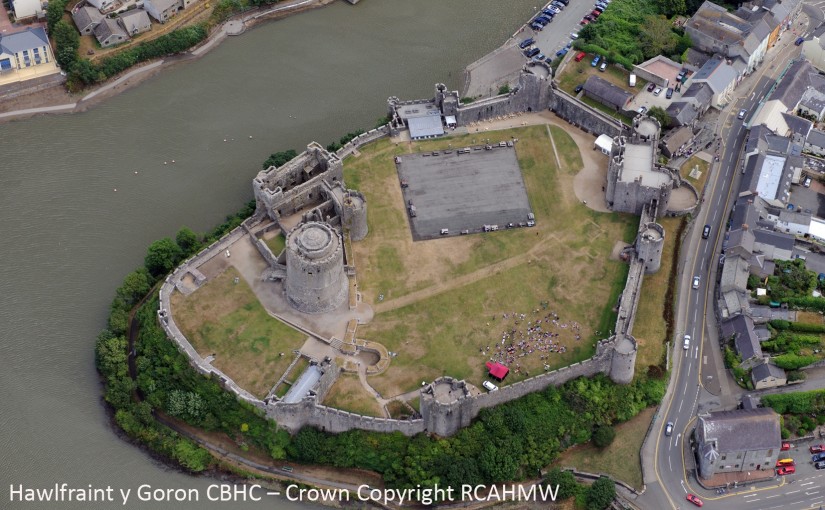
Every September thousands of historic sites in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland are opened. It is a chance to visit some sites which are closed the rest of the year. You can find out more details online. Here are four places to get you started.
Broughty
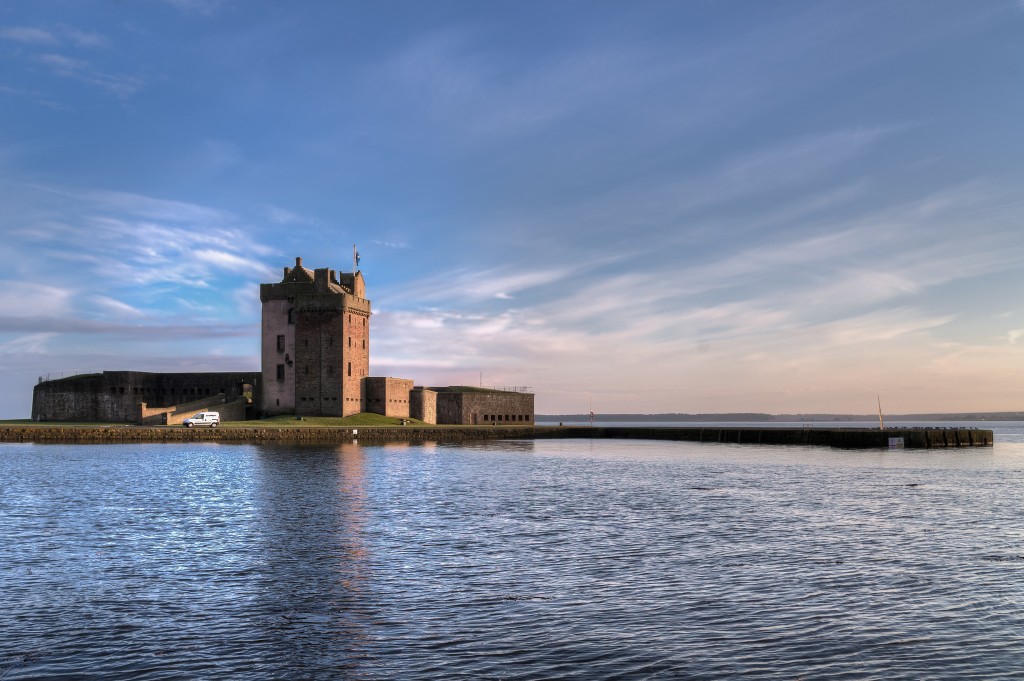

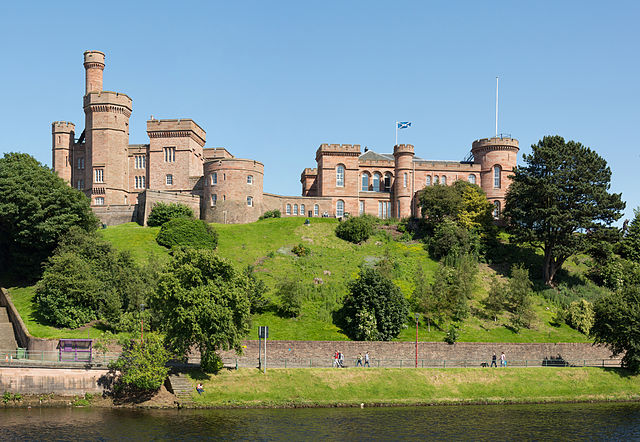
Sat on the banks of the River Tay, Broughty Castle in Scotland was built in 1496. It was involved in several sieges including during ‘the Rough Wooing’ and the War of the Three Kingdoms. The castle has been open as a museum since 1969.
Broughty Castle is open from 1pm to 3pm on Sunday 18th September.
Pleshey
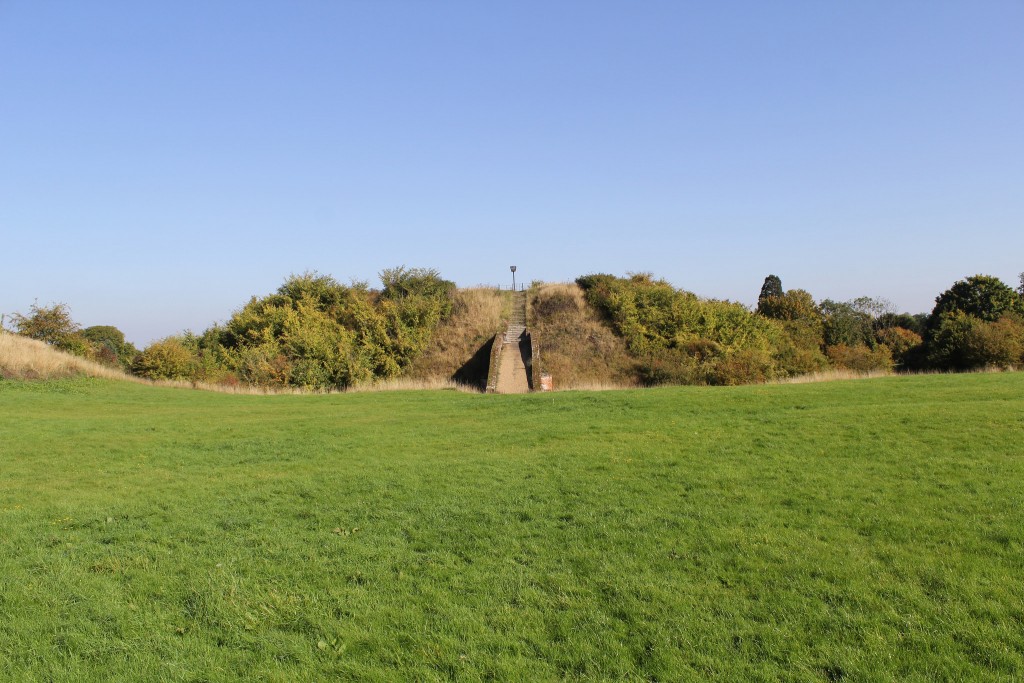

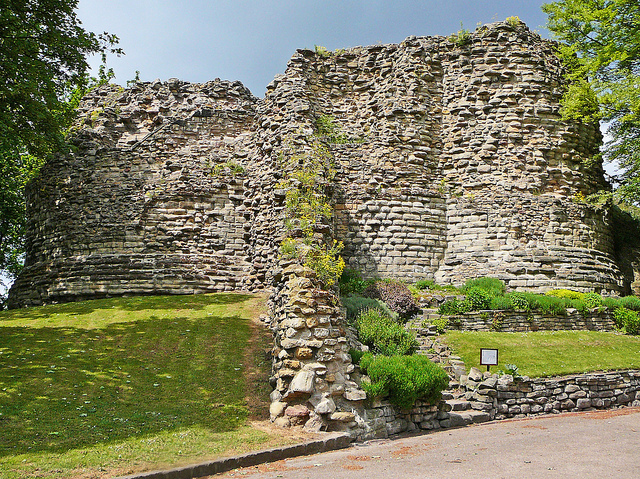
Pleshey Castle in England was built by William de Mandeville, one of the richest men in 12th-century England. It was confiscated by the king, slighted, restored, and used for centuries afterwards. The castle was even mentioned in Shakespeare’s Richard II.
The motte-and-bailey castle survives as some impressive earthworks. Excavations were carried out between 1972 and 1981 but never published. In 2015 the Trust funded part of the publication of the work from this important site.
Pleshey Castle is open on Sunday 11th September with tours at 2pm, 3pm, and 4pm. Advanced booking is required.
Moyry
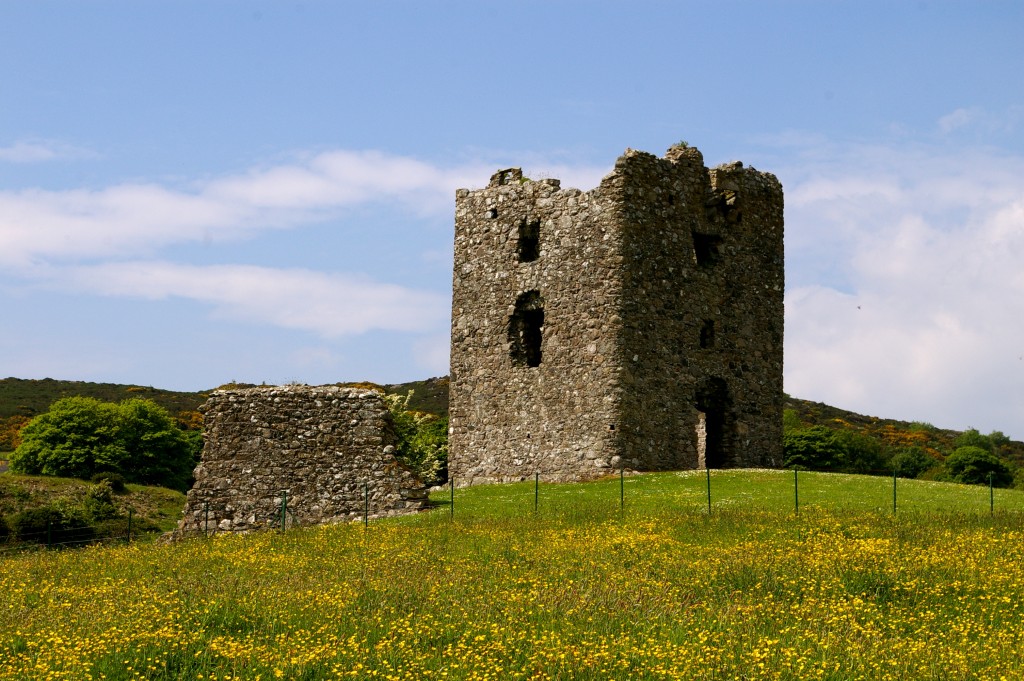

Built in 1601, Moyry Castle is being included in Northern Ireland’s heritage open days for the first time. Three-stories high and perched on top of a rocky hill the castle has a good view of the surrounding area.
Moyry Castle is open from 9am to 8pm on Saturday 10th and Sunday 11th September and is free to visit.
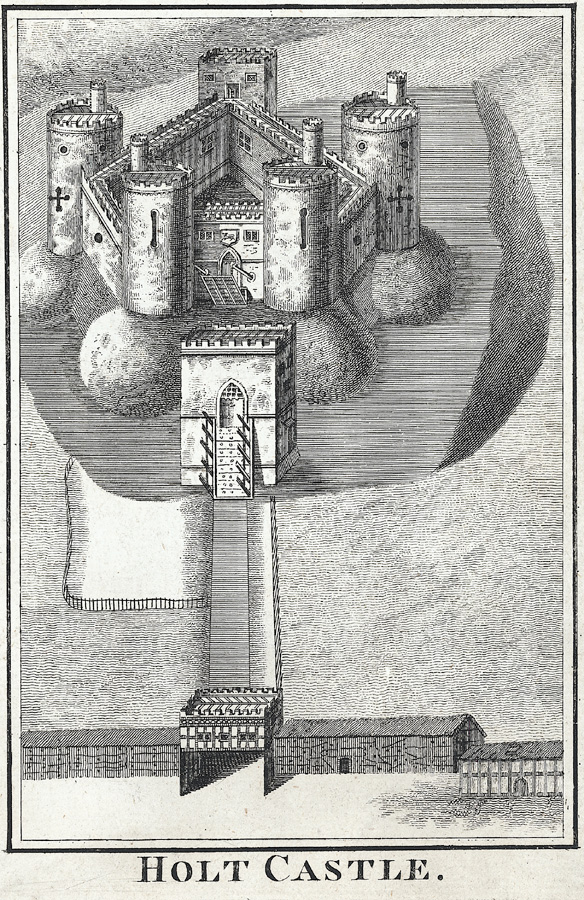
Holt

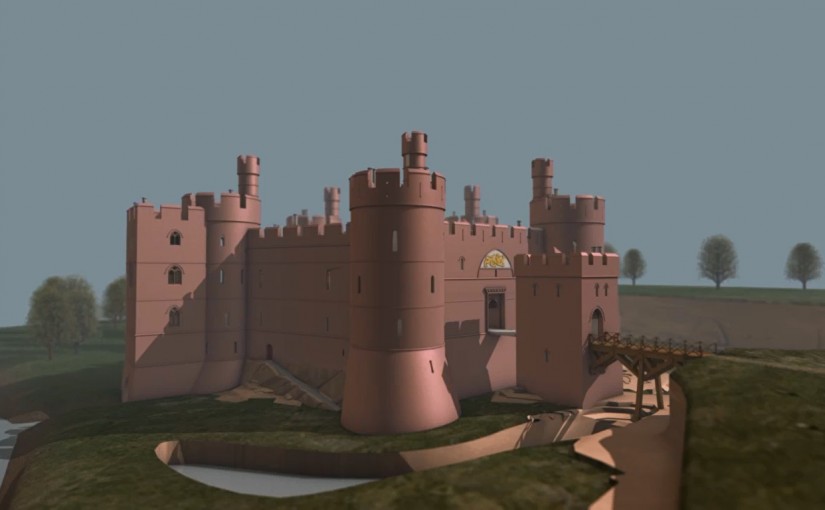
Constructed in the 13th century, Holt Castle was amongst the fortifications built by the English in north Wales. The red sandstone makes the castle stand out, as does its unusual pentagonal design. It was used by Richard II as a treasure house and slighted after the English Civil War.
You might recognise Holt as one of the very first projects the Trust worked on: Rick Turner and Chris Jones-Jenkins created a reconstruction of the castle as it would have appeared c1495. The 17th century was not kind to the castle, so the reconstruction is worth watching to get an impression of how it looked.
Holt Castle is open from 10am to 4pm on Saturday 17th and Sunday 18th September and is free to visit.