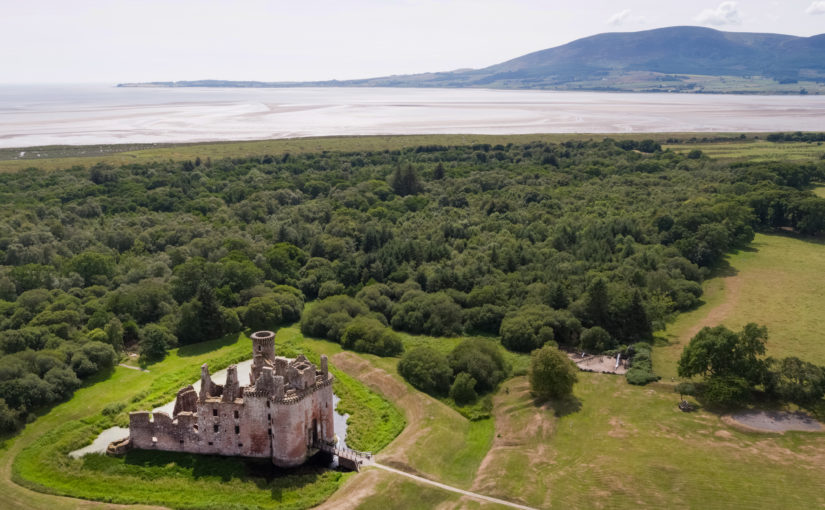
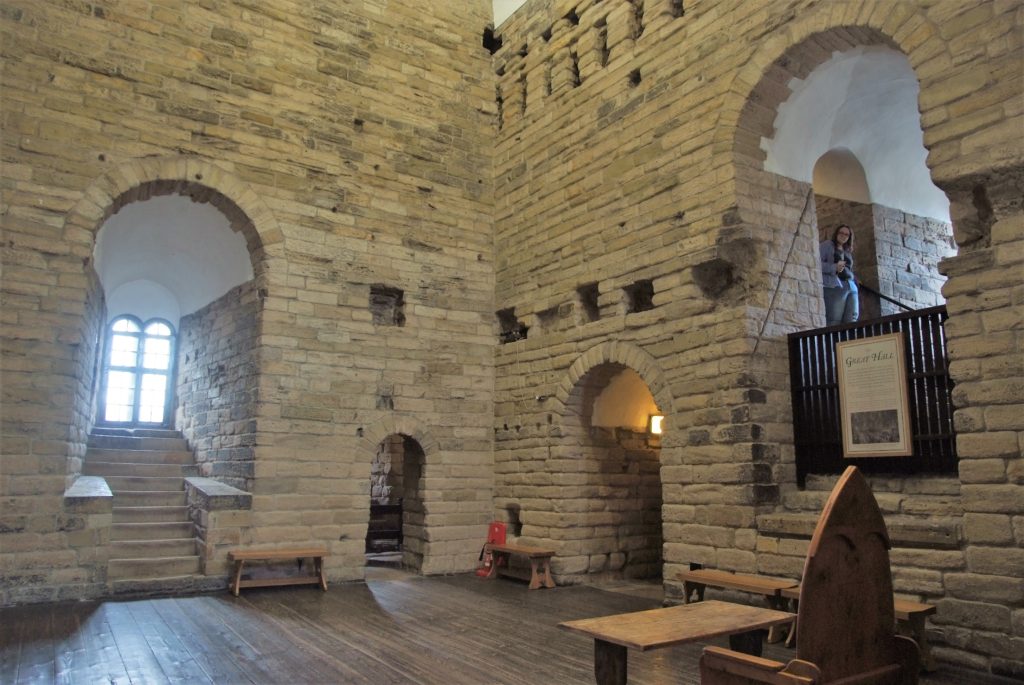
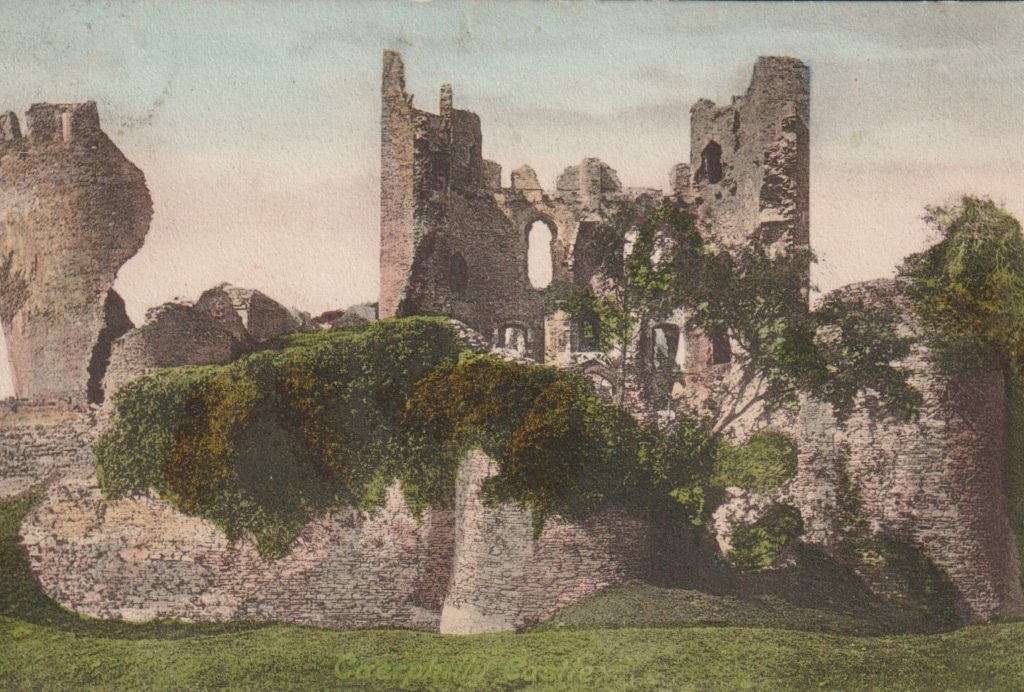
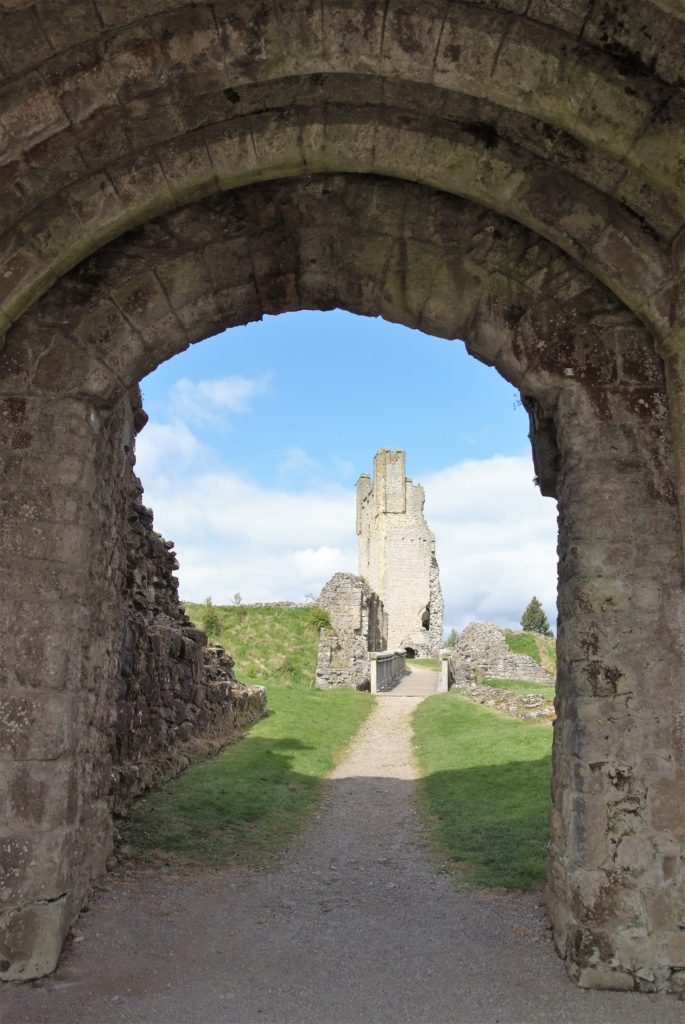
Project lead, Dr Richard Tipping, looks back at the first of the two weeks of fieldwork he and Dr Eileen Tisdall are undertaking to try establish whether climate change did impact the re-positioning of Caerlaverock Castle.
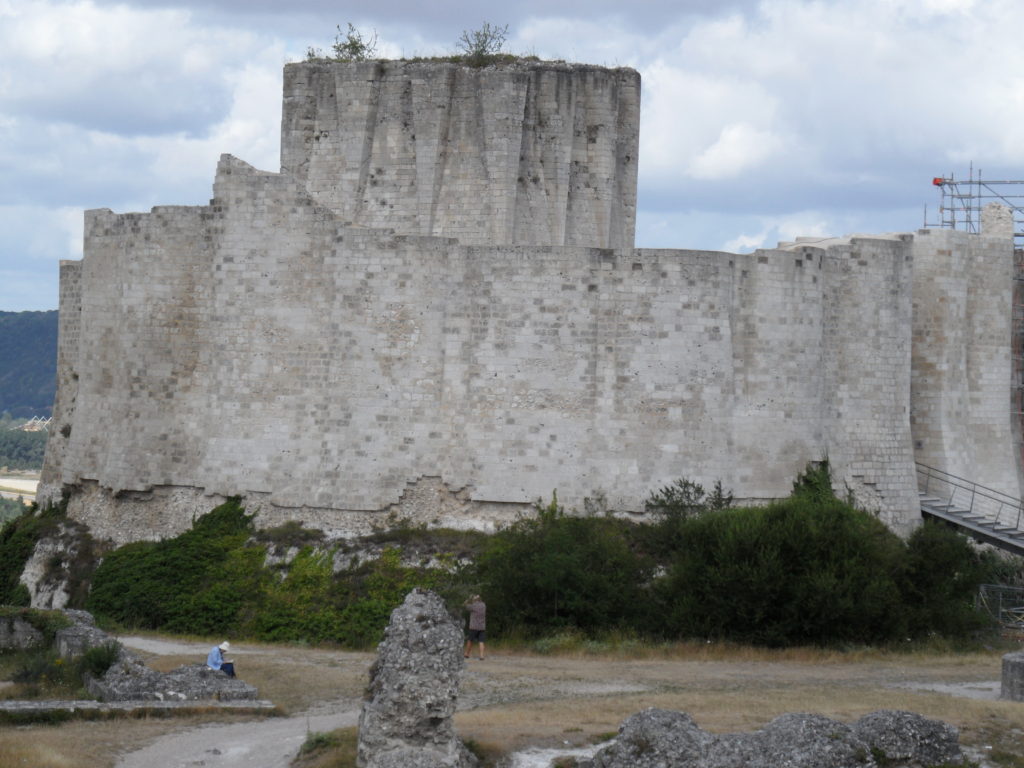
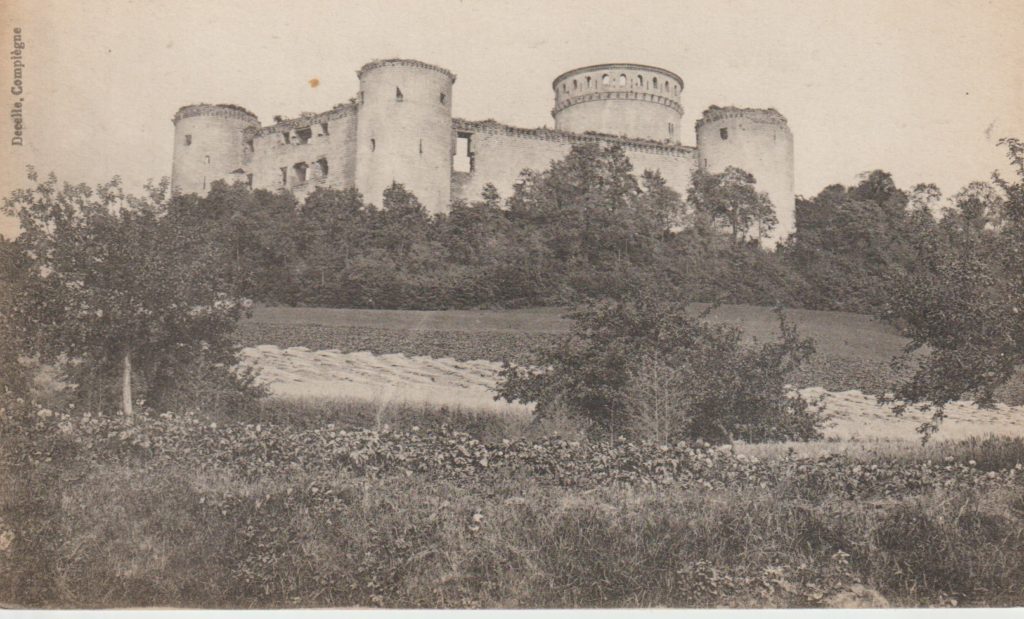
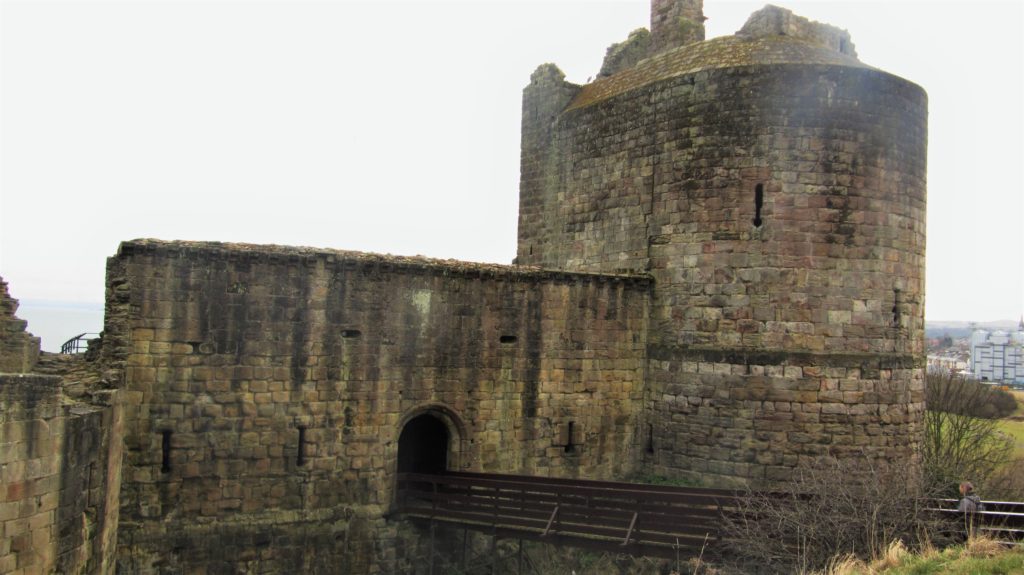
Well, somewhat later than planned or advertised, the first week of fieldwork at the old castle at Caerlaverock began on 3rd July. It has been dated by oak tree rings from the drawbridge across the moat to c. AD1229. The new castle, a couple of hundred metres away and upslope, began construction only 50 years later. Why the rebuild? This is the mystery.
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
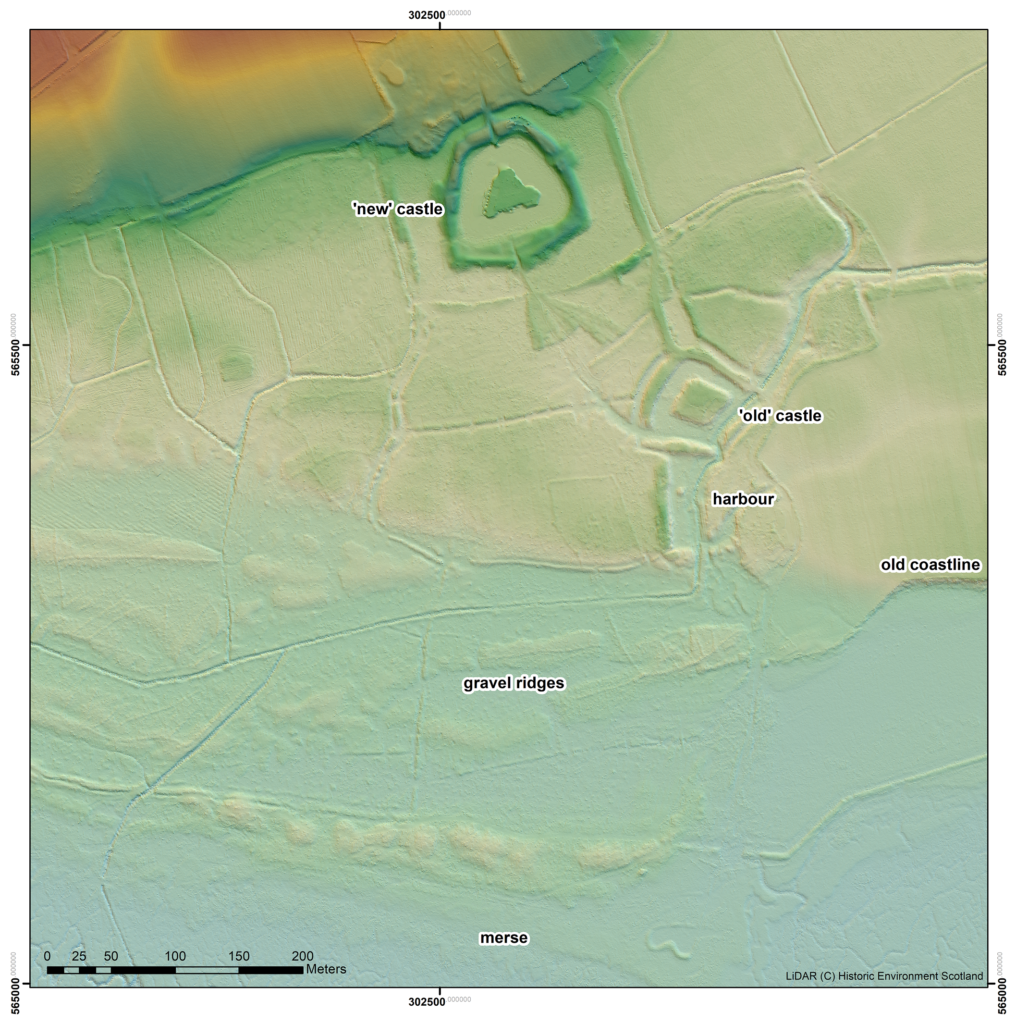
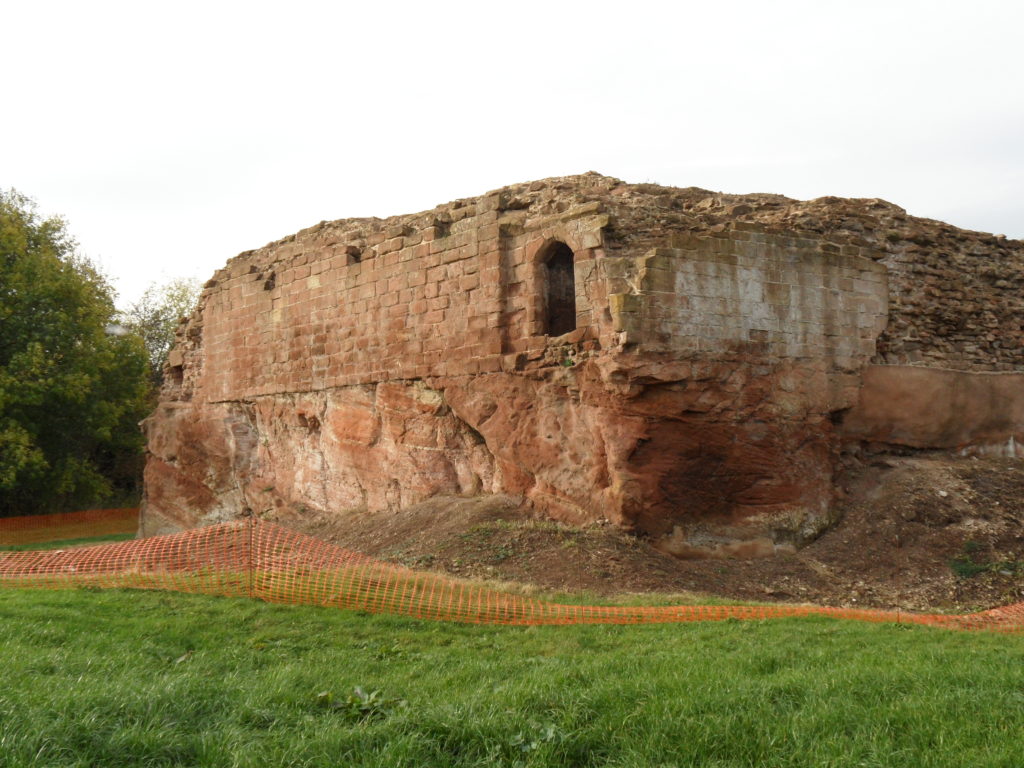
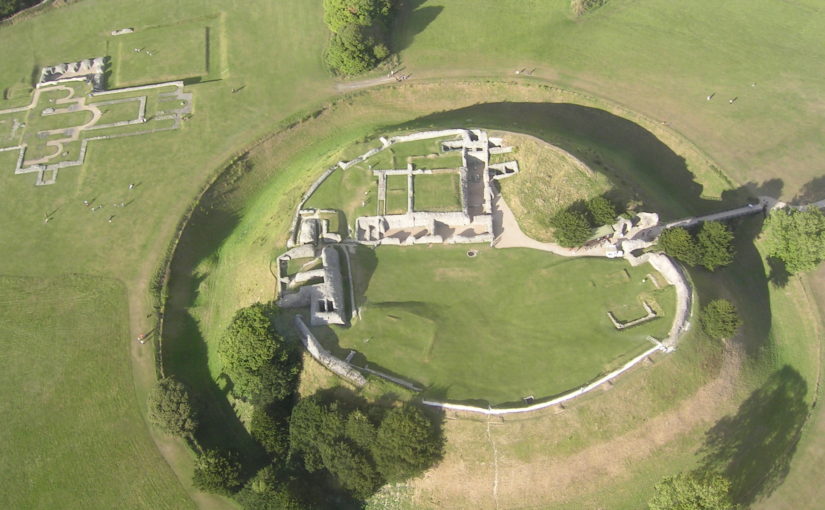
The natural environment played a role. Some archaeologists think the old castle started to fall apart because it was built on soft sediment, a deep clay-rich silt locally called ‘carse’. And sure enough, the new castle was built on the nearest outcrop of bedrock. But twenty years ago, a team of environmental archaeologists from the Universities of Stirling and Coventry found an additional reason for abandonment of the old castle. They found, in a wide ditch next to its moat, a thick layer of grey estuarine-marine mud penetrating the brown freshwater peat of the ditch. This suggested that very large storm surges impacted the environs of the old castle. Further work found very large gravel beach ridges, thrown up in these storms, stacked against the old shoreline.
That team included Dr Richard Tipping and Dr Eileen Tisdall from the University of Stirling. Now we are back to find more evidence and improve the dating of the sediments funded by the Castle Studies Trust, as Historic Environment Scotland, the custodians of both castles, seek to update what we know of Caerlaverock and improve the visitor experience.
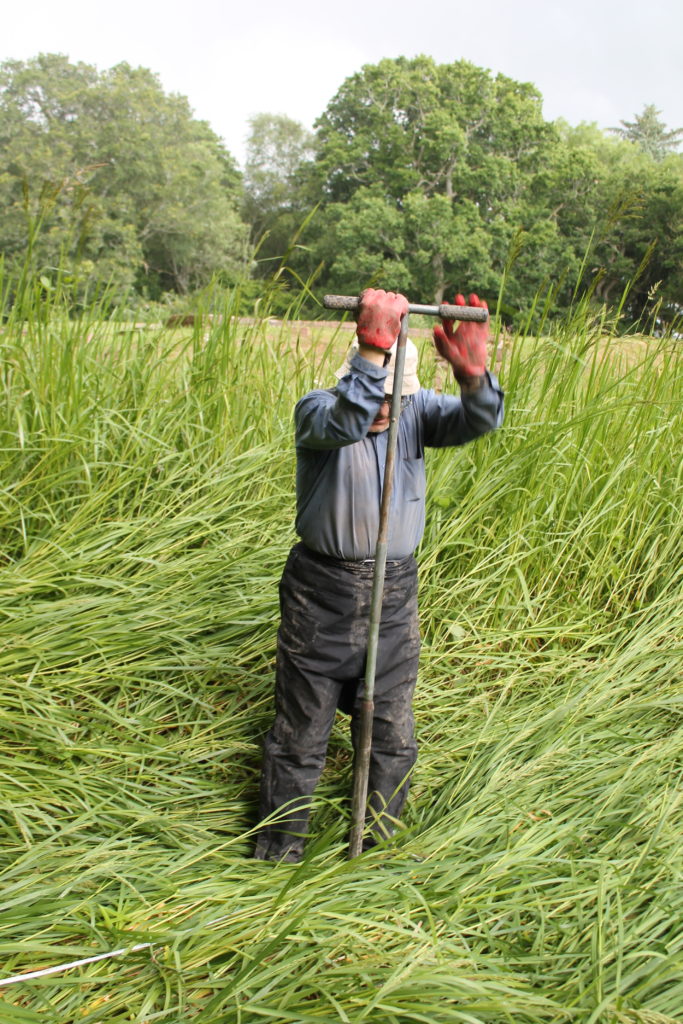

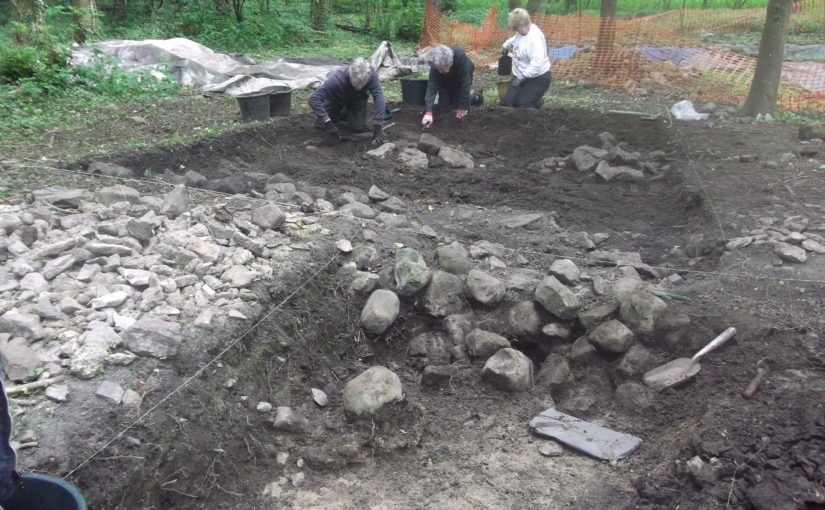
For a week, 3rd-10th July, Richard Tipping stuck tiny (2.5cm diameter) holes in sediments in the ditches and moat with a simple corer, a metre-long metal gutter with a handle on the end. Push it in, turn it around to cut out a sample and pull it out, together with a metre of sediment. Record the sediment and then repeat, usually in a straight line called a transect. He did this over 80 times in the week. Isn’t science exciting? It wasn’t too hard: the sediments in the ditches and moats are less than a metre thick before the ‘natural’, as archaeologists call it, the sterile silt of the ‘carse’. But because the sediments are so thin, and because we knew that they recorded a lot of environmental ‘events’ in a short period of time, logging the cores in detail took time. A challenge, too: there are only so many shades of grey or brown.
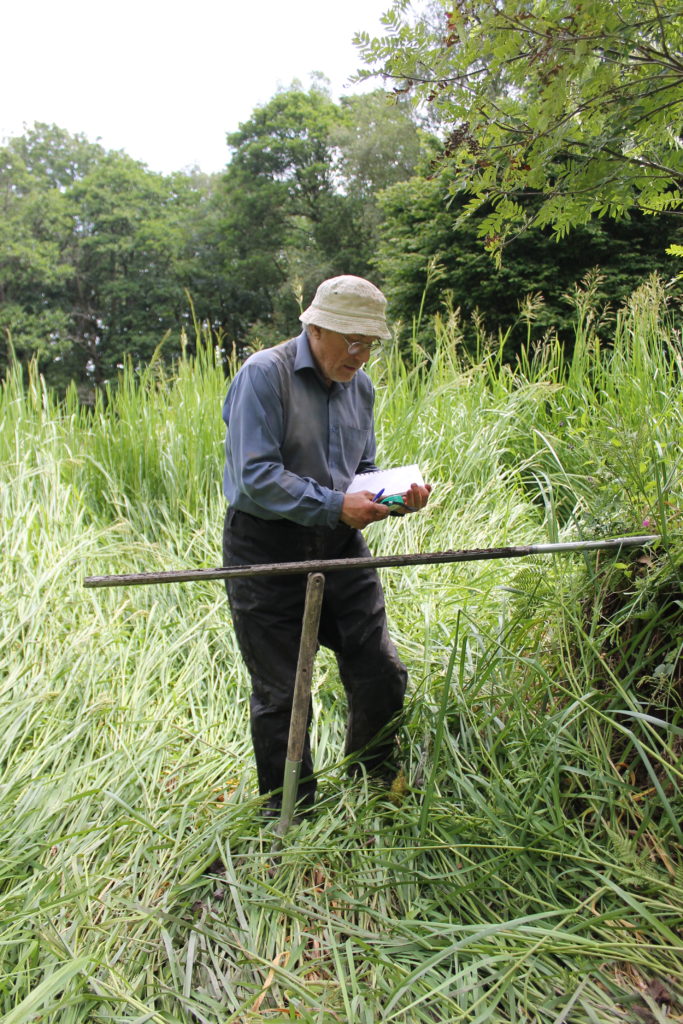

Coring started in the artificial ditch that runs parallel to the moat. This was where we first began, twenty years ago, to realise that something funny was going on; in fact, several funny things. Why, in the first place, dig a 60 m long, 3 m wide ditch alongside one side, and only one side, of the moat? Twenty years ago, radiocarbon dates on freshwater peat at the base of the ditch hinted that this ditch was actually earlier than the old castle, maybe 200 years earlier. We aim to clarify this. Coring found the same sediments we found last time, which is always reassuring. Peat at the base of the ditch was replaced by grey silt. This was sealed by more peat. There is more grey silt at the end of the ditch nearest the coast, although the upper layer penetrated the full 60 m length.
We could not understand, twenty years ago, the filling of the moat with sediment: too few boreholes, too far apart. This time, cores were spaced 1.5 to 3 m apart along a 40 m long line. Archaeologists generally excavate and record continuous sections. We can’t do this because the site is a Scheduled Monument, and besides, the sediment is under water (though this week mercifully dry underfoot), so we construct our section from transects of cores, ‘joining up the dots’ by correlation. For the first time we can show that the moat was probably affected by the same environmental impacts that hit the parallel ditch. This is only ‘probable’ because radiocarbon dating has yet to show the events are the same. But grey silt entered the moat from the coast, pushing up the moat, probably eroding earlier-formed peat but not penetrating the full length. At the end farthest from the coast, near the bridge, peat continued to form.
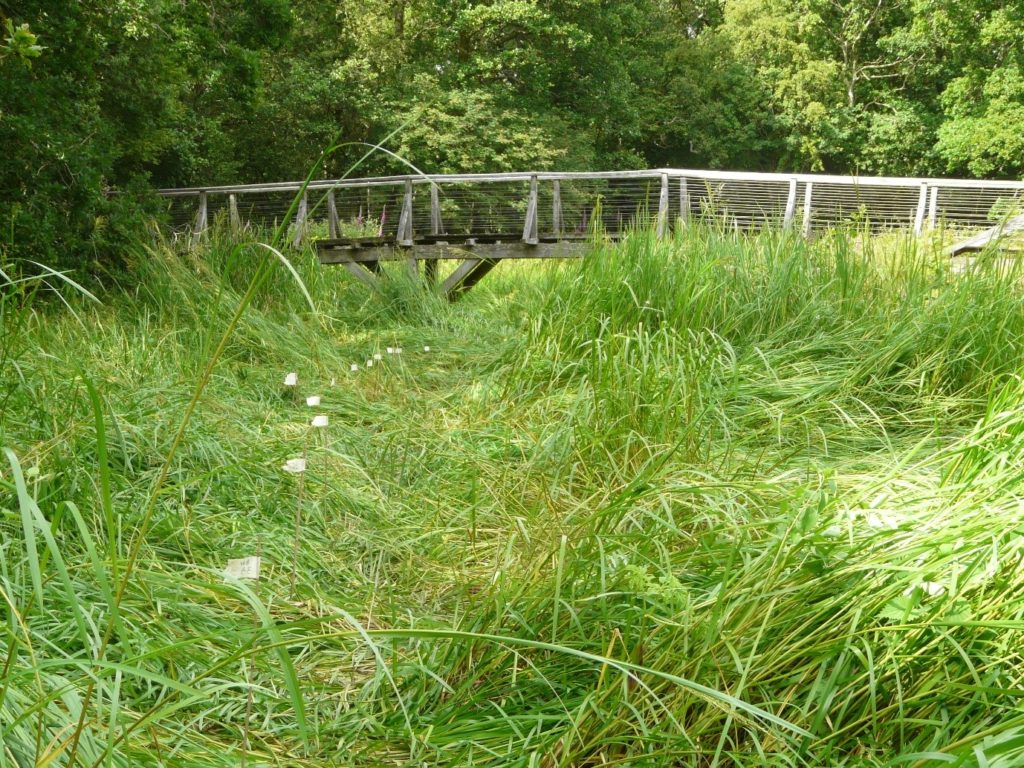

Our cores also revealed two new aspects of moat construction. The first is that the constructors took a shortcut in making the moat. In two arms of the moat, they had incorporated natural stream channels in the moat, twice as deep as the rest of the moat. This was a way, of course, to ensure the moat was under water. But away from these channels, the ‘natural’ lay only 20-40 cm below the present sediment surface. If the water surface then was as it is now, the depth of water would have been barely above the knee. You might have waded to the castle rather than use the drawbridge.
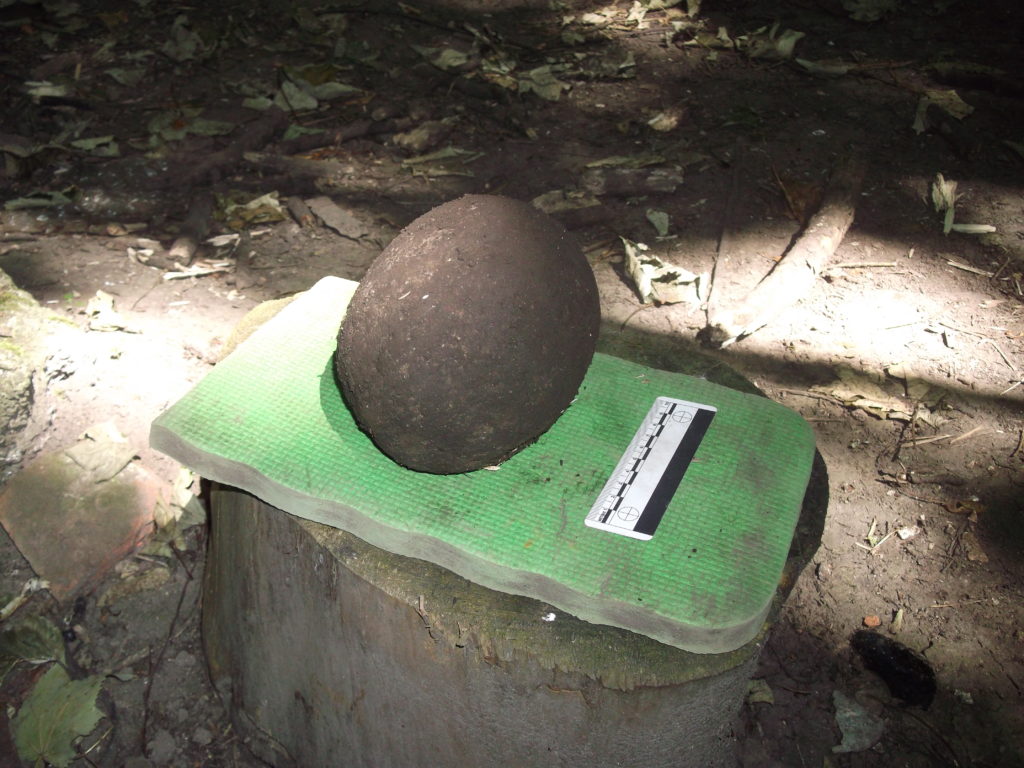
Coring in parts of the moat also hit stone at shallow depths. The carse itself is stoneless, and so the stone was emplaced by people. Stabbing around with the corer revealed these stones to be large blocks. They are concentrated at one corner of the moat, nearest the coast. Maybe they were buttresses put in to strengthen the foundations of the castle, either as it started to subside, or maybe undermined by storm surges.
Now I’m thinking and planning the next part of the campaign, straightening my back, and hoping the insect bites subside: the joys of fieldwork. From 17th July we start again, for a week, away from the old castle and out onto the old beach ridges and the basins formed by them. In the early 2000s, tree-felling of Sitka spruce allowed us to see what we were doing. Now it’s a dense tangle of semi-natural oak woodland and not easy to move around in. Wish me luck!