Castle Studies Trustee Charles Hollwey looks at the intriguing case of Humphrey de Bohun and the 10 licences to crenellate awarded to him on the eve of the Black Death and what happened to them.
In December 1347, Humphrey de Bohun, 6th earl of Hereford, 5th earl of Essex, was given a licence to crenellate, i.e. to fortify, 10 of his manors. These were:-
- Writtle, Brymshoo, Apechilde, Depeden, Saffron Walden; Essex
- Enfield; Middlesex
- Oaksey, Upavon, Seend; Wiltshire
- Whitminster; Gloucestershire
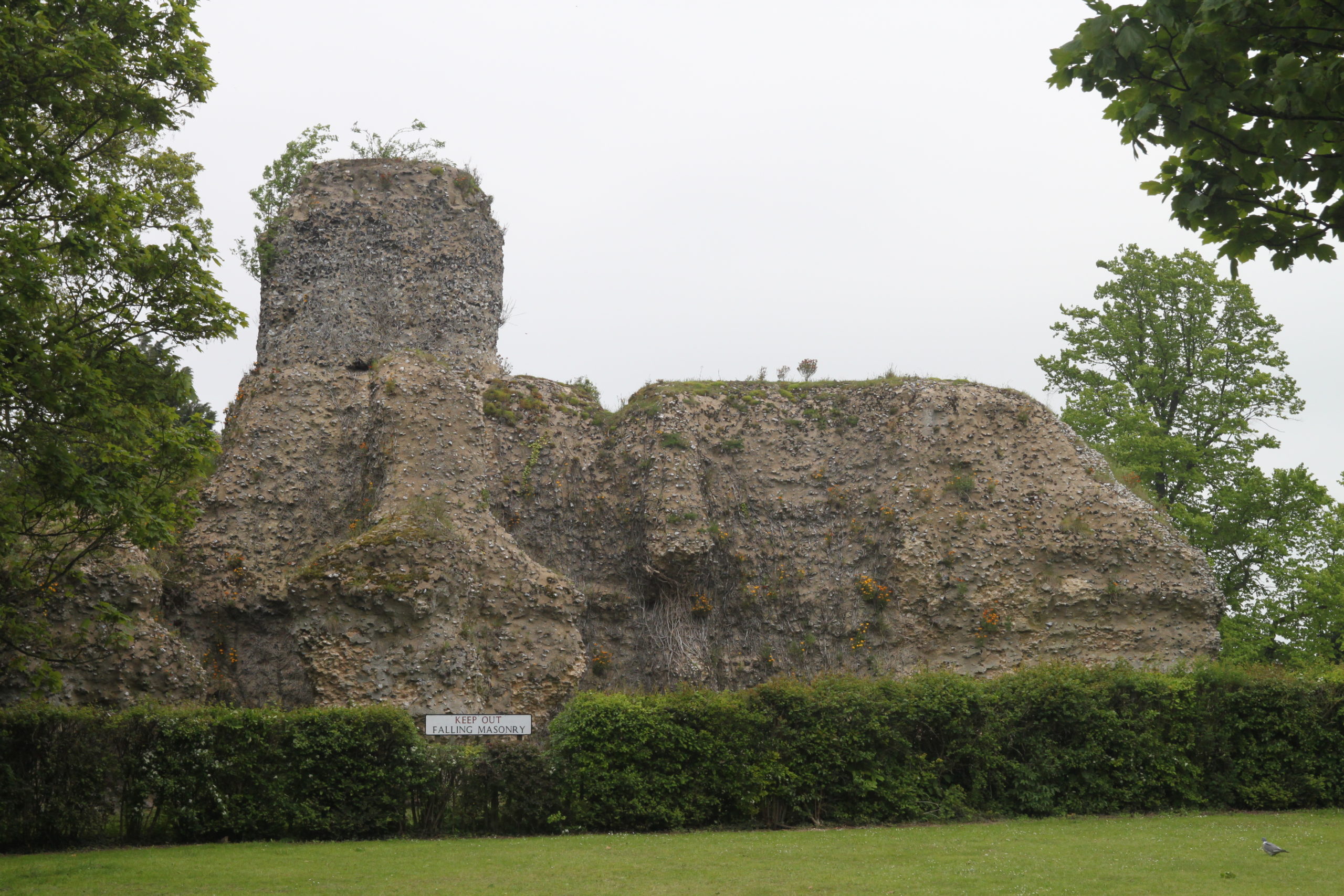
The number of licences is the most ever given, at one time, to a medieval noble or gentry. You can find them all on the Gatehouse castle gazetteer website[i]. However scrutiny here would indicate that there is little to see now or indeed was in the past. Most of the sites would appear to have been not much more than lightly fortified manor houses. Only at Saffron Walden is there what would be commonly described as a castle. However here and elsewhere there is little evidence that any building work was done by Humphrey.
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
A possible explanation could be the date. In 1348, the Black Death reached England. It was first recorded at Weymouth in June, reaching London by the autumn and was across all southern England by March 1349. It was only in December 1349 that some form of normality returned.
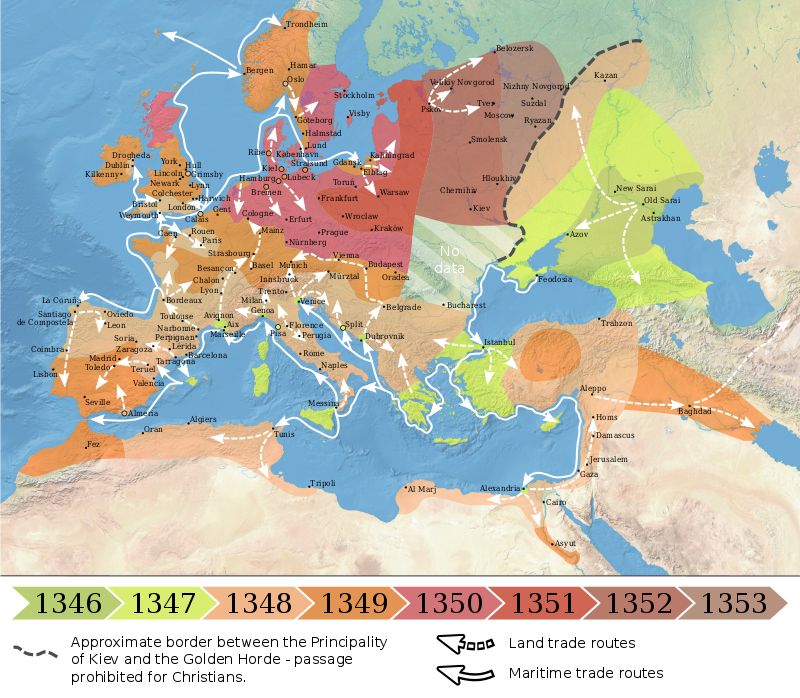
Like our current pandemic there were drastic consequences with an estimated 40 to 60% of the population dying, the greatest loss being amongst the working classes. There was a curtailment of much activity for instance major campaigns in the 100 Years’ War with France were halted until 1355. Post the pandemic there was a shortage of labour with an increase in wages, meaning building projects would have been more expensive.[ii]

In such a situation did Humphrey cease his building plans? Before jumping to this conclusion we need to probe into the impact on castle construction, the nature of licences to crenellate and the life of Humphrey.
- Impact on castle building? The consensus view seems to be, certainly in the long term, this was not great. John Goodall, the eminent castle expert suggests it raised the financial threshold of construction and increased the relative importance of royal works. However it did not “deter the very richest—from embarking on splendid building projects”[iii]
- Nature of licences to crenellate? It is not unusual to have licences without ensuing building work. The research of the late Charles Coulson and Phil Davies has highlighted that the true nature of such licences was not to control castle building but for the recipients to obtain the prestige, status and legitimacy of having such documents, whilst also generating revenue to the crown.[iv] Many were made after castle building or were given to buildings with minimal fortifications and many seemed to have led to no construction. The number given to Humphrey whilst high was similar to a few Bishops, for instance the bishop of Salisbury received licences for 10 sites in 1377 and the bishop of Chichester for 12 houses in 1448. Similarly to Humphrey, there was little consequently to see.
- Life of Humphrey? Born in 1309 a younger son, inheriting in 1336, he served in the Breton campaigns of the Hundred Years’ War with involvement in the victories of Morlaix (1342) and La Roche-Derrien (1347).[v] However I am unaware of any subsequent campaigning and despite being the Lord High Constable of England he was never a favourite of Edward III. He died in 1361 at Pleshey Castle leaving his nephew as heir.
There is not a simple answer to this plethora of licences and missing castles. It is possible some were to underpin his legitimacy to manors where his inheritance might have been disputed, such as Seend and Upavon. Similarly at Saffron Walden, which had been slighted as a castle during the anarchy. Others might have been to emphasis his premier noble status.
Perhaps what was important pre-pandemic was not so afterwards? The impact on his psychological wellbeing is unknown but might be significant as can occur in our pandemic. In 1350 he commissioned the translation of the romance poem ‘Guillaume de Palerme’. He did not seem to have married or had children.
In my view the answer to this mystery is not simply the pandemic but it might have been a factor. I do think more understanding of his life might be the key.
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
Featured Image: Walden Castle, Saffron Walden, slighted during the anarchy.
Footnotes
[i] www.gatehouse-gazetteer.info
[ii] Black Death in England Wikipedia
[iii] Goodall, John (2011), The English Castle, Yale University Press, p 258
[iv] Davis, Philip (2009), ‘Licences to Crenellate‘, Castle Studies Group Journal 22
[v] Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). “Bohun“. Encyclopædia Britannica. 4 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 138.
All pictures sourced from Wikimedia Commons; Links, attributions and licences as follows
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Walden_Castle_in_Saffron_Walden.JPG
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1346-1353_spread_of_the_Black_Death_in_Europe_map.svg
