The deadline for grant applications passed on 15th December. We’re going through the various projects now. Altogether the 15 projects, coming from all parts of Britain, are asking for over £63,000. They cover not only a wide period of history but also a wide range of topics. For a little more detail, here are the applications we’ve received:
- Caldicot, Wales – a geophysical survey of the scheduled area of Caldicot Castle using magnetometry, resistivity, and Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- Dig It! 2017 Castles of South Scotland – enhancing public understanding and knowledge of some castles in southern Scotland, their purpose, their history and their relevance, particularly the lesser-known and least visited sites.
- Dunyvaig, Scotland – co-funding a project to provide better understanding of the landscape context of the castle by conducting detailed topographic and geophysical surveys and carrying out trial trenching to gain key information regarding the preservation and the depth of the buried deposits.
- Keith Marischal, Scotland – geophysical survey at Keith Marischal House, in search of a lost medieval castle and renaissance palace with a great hall reputed to be second in size to that of Stirling’s.
- Lathom, England – excavations to find out the true size of Lathom Castle. You may recognised them from 2017’s grants when we funded analysis of masonry recovered from excavations between 1997 and 2009.
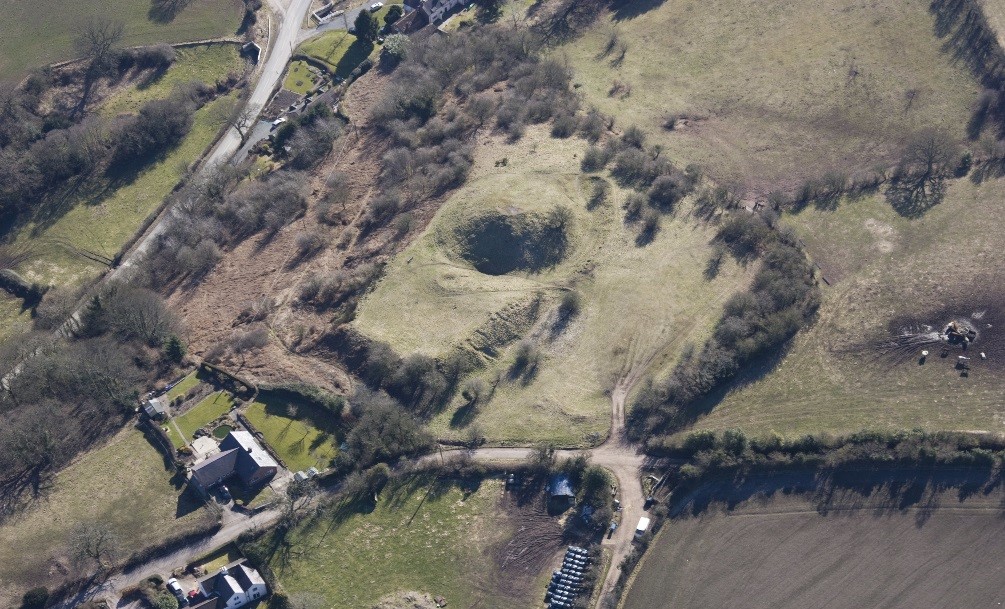
- Laughton-en-le-Mortain, England – comprehensive archaeological investigation of the motte and bailey castle of Laughton-en-le-Morthen, South Yorkshire and its surrounding landscape.
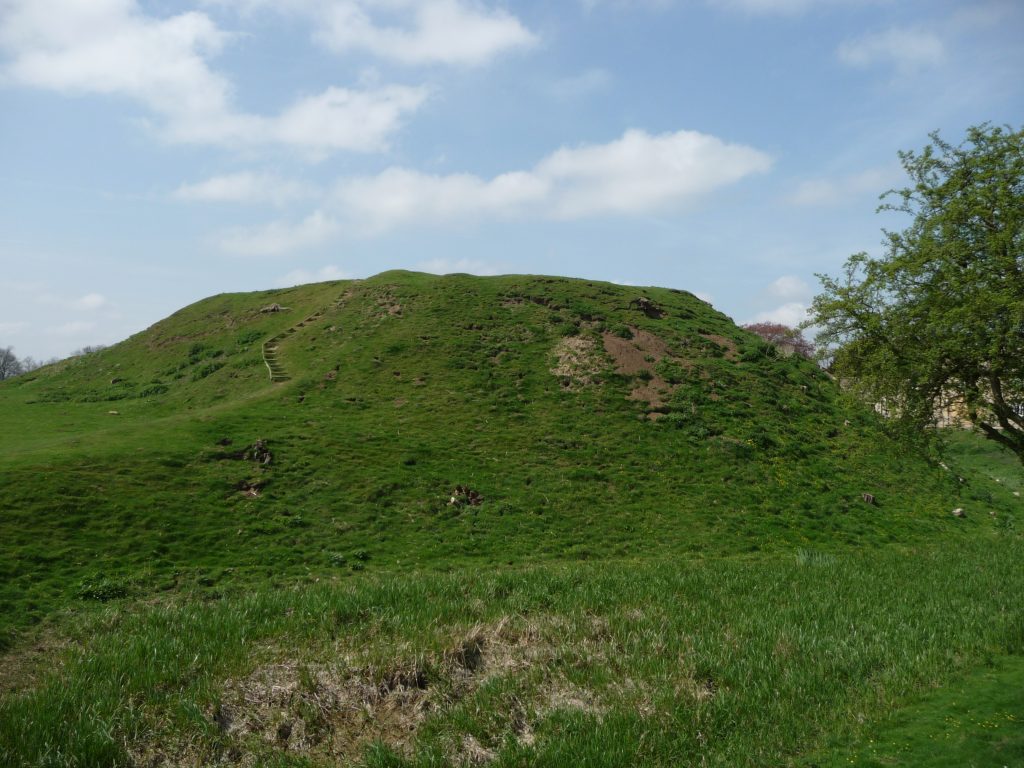
- Loch Kinord, Castle Island, Scotland – radiocarbon dating an early island castle: Castle Island, Loch Kinord, Aberdeenshire
- Old Bolingbroke, England – revealing the history of Old Bolingbroke’s Castles: What can researching Bolingbroke Castle’s Route Yard and Dewy Hill tell us about Bolingbroke Castle?
- Pembroke, Wales – test trenches at one of Wales’ greatest castles to confirm the site of the late medieval structure revealed in the geophysical survey funded by the CST in 2016.
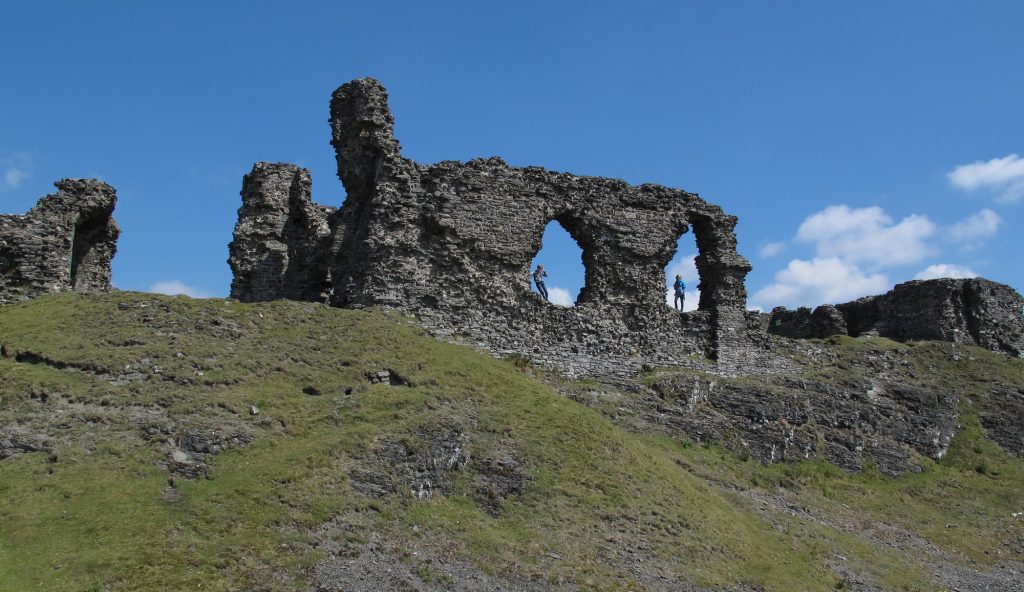
- Ruthin Denbighshire – co-funding reconstruction drawing of this great Welsh Edwardian fortress. Ruthin was the town where Owain Glyndwr’s rebellion against English rule started.
- Sheffield, England – record and examine the architectural fragments stored on the site of the castle found in previous excavations.
- Skipton, England – an archaeological/architectural survey will be produced of the gate structures and flanking round towers of the inner ward of Skipton Castle.
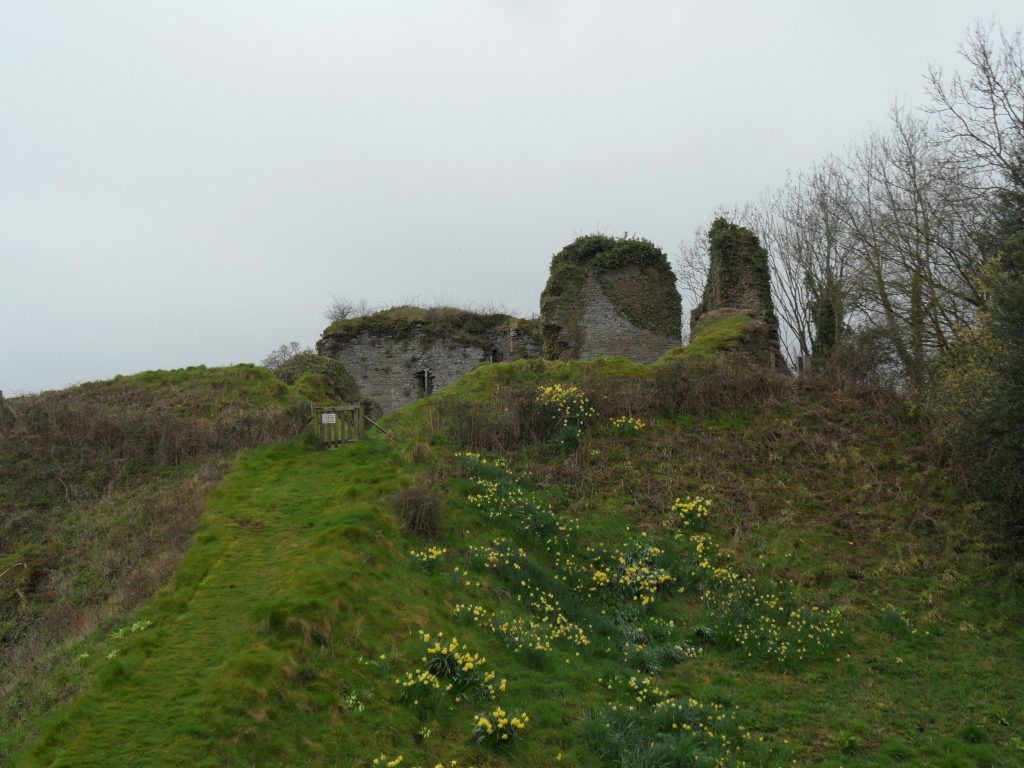
- Snodhill, England – geophysical survey and excavations to answer some key remaining questions of this important Welsh border fortress re: the castle namely where was the entrance and function of the North Tower.
The applications have been sent to our expert assessors who will go over them. You can see how the assessment process works in one of our earlier blogs.