The Castle Studies Trust is delighted to announce the award of six grants, totalling a record £31,000 not only covering a wide geographic area but also a wide range of different types of research:
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
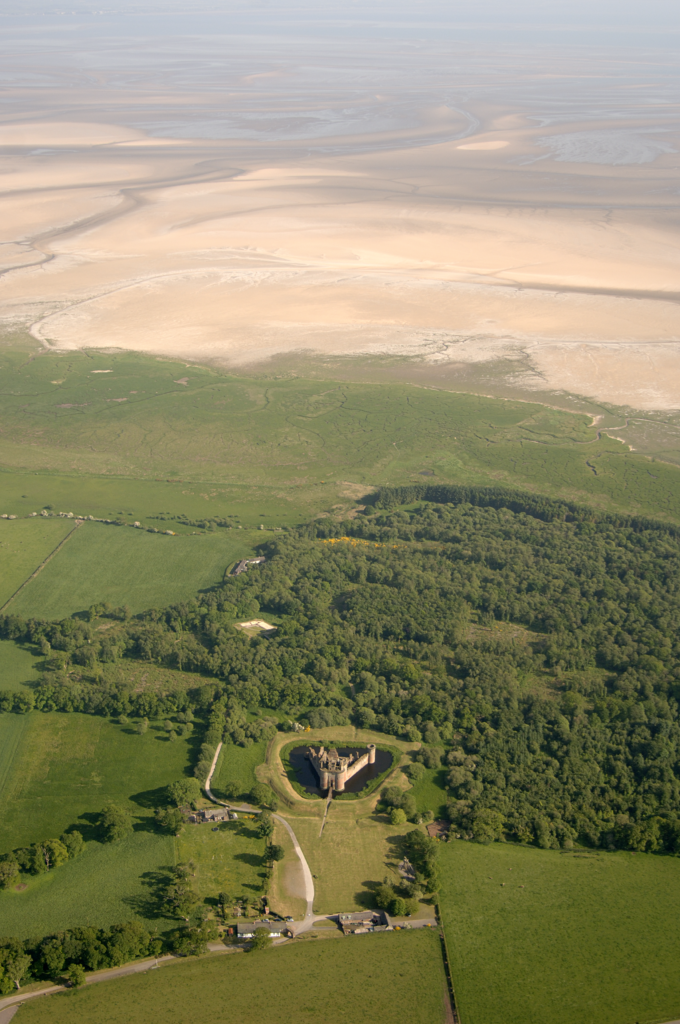

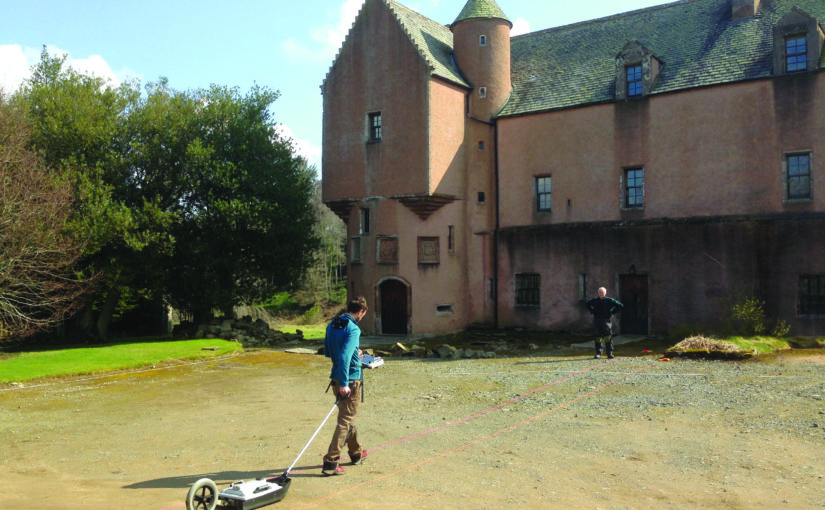
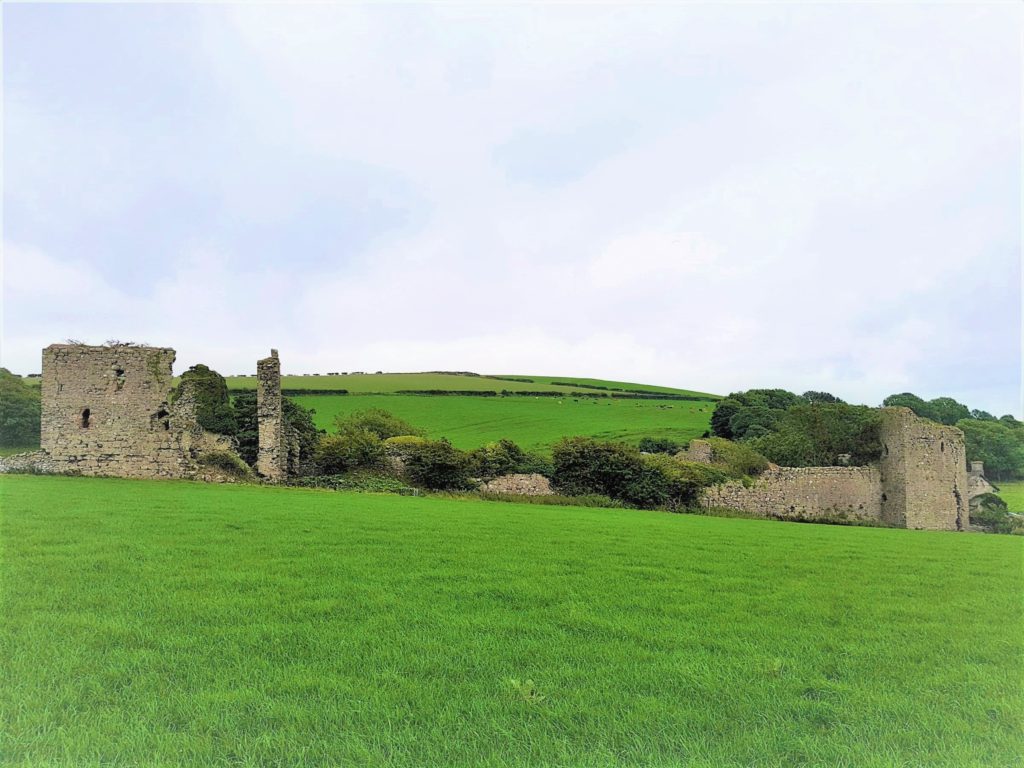
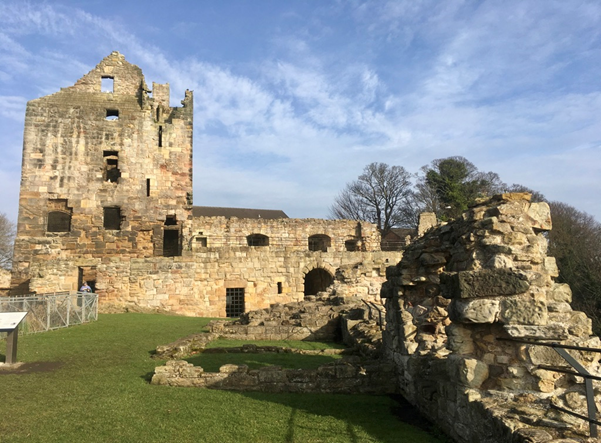
Caerlaverock, Dumfriesshire
The aim is to understand the chronology and geography of extreme weather events in the high medieval period, and the effects they wrought on archaeological features that led to the abandonment of the old castle built in c.1229 in favour of the new built 200m away in c.1277. The latest thinking is that it was a series of extraordinary storm surge events which pushed a series of storm driven gravel ridges across the River Nith.
The methodology to find this out is interdisciplinary, using scientific methods to enhance understanding of archaeological fieldwork. The fieldwork will involve the establishment of a series of transects across the site and surrounding landscape from which cores and samples will be extracted for sediment description, stratigraphic analysis, and Carbon 14 dating.
Depending on Covid restrictions, the aim is to start doing the work in May this year with the receipt of the final data in the autumn.
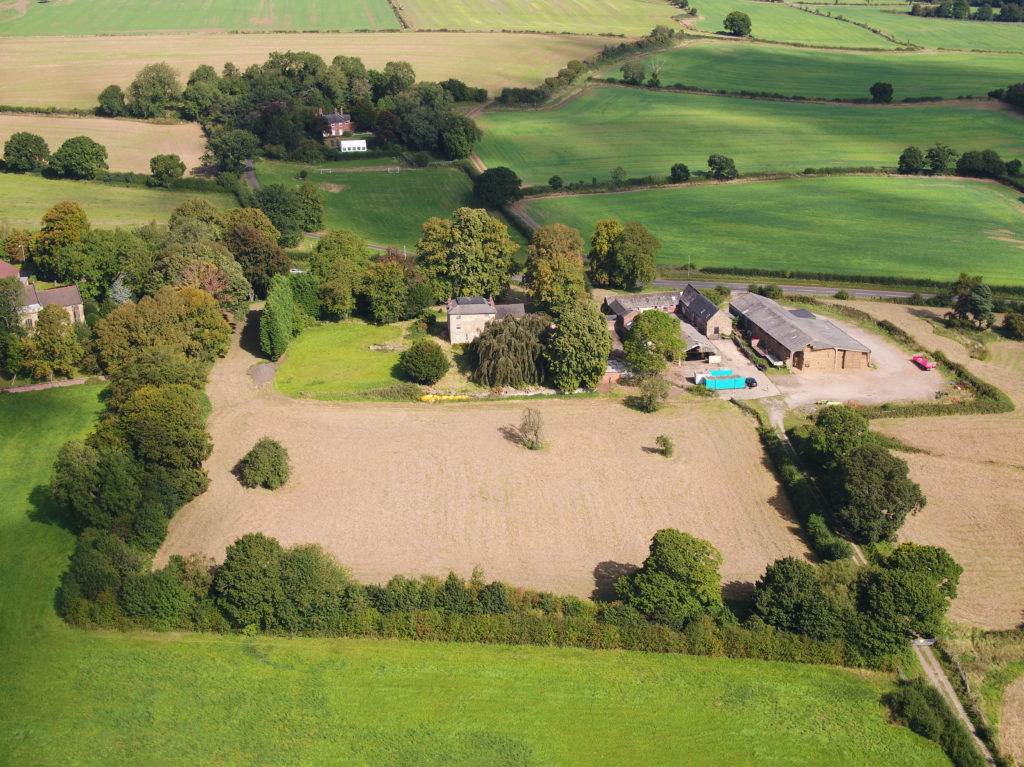

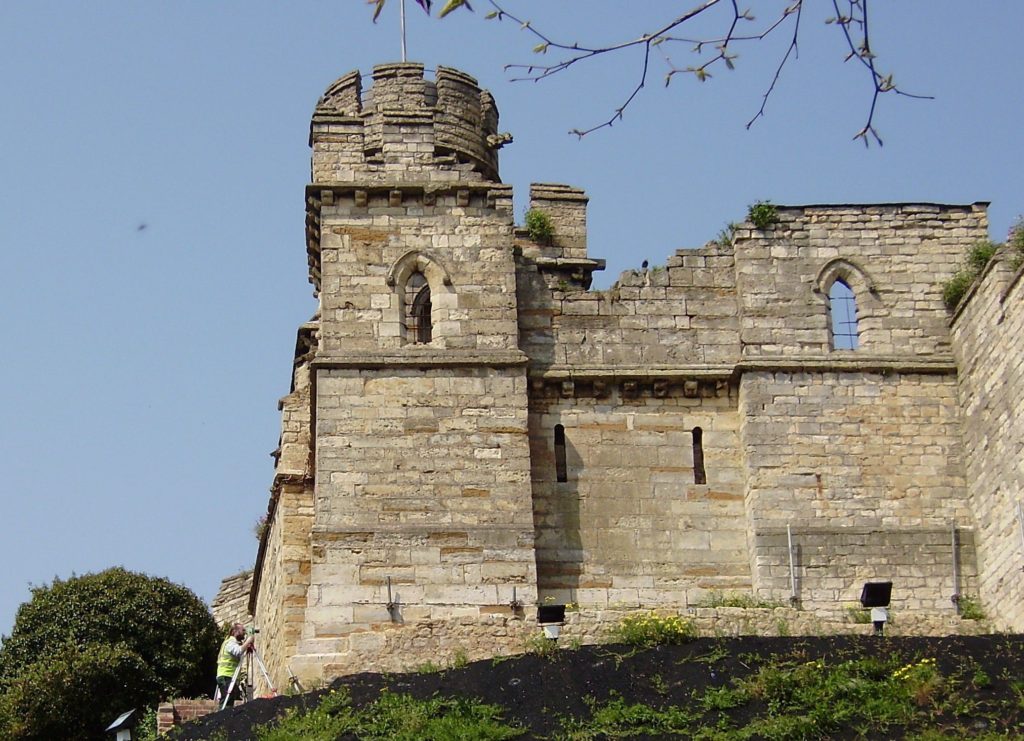
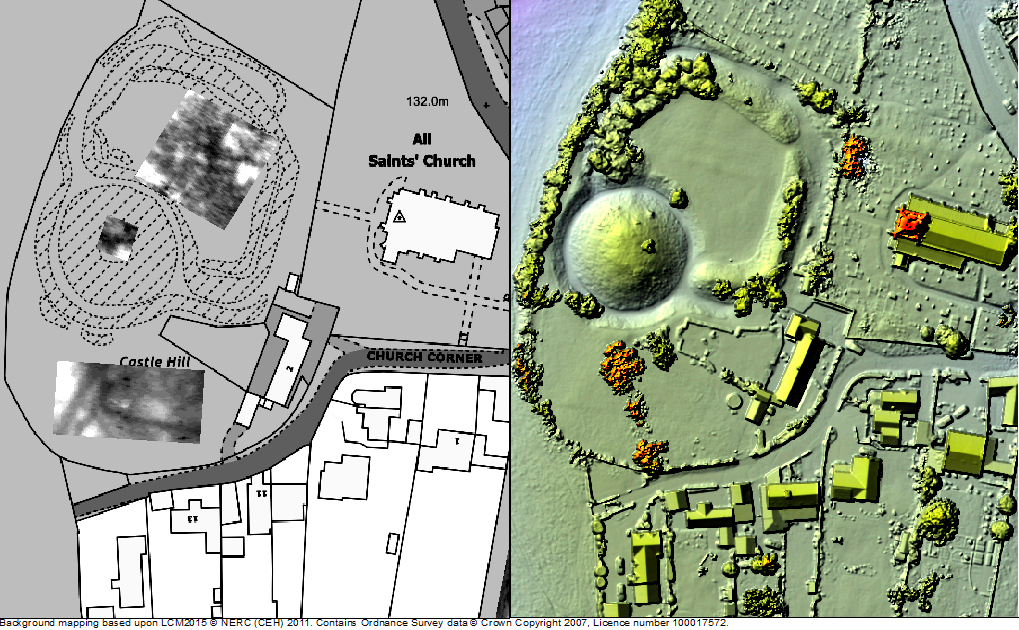
Greasley, Nottinghamshire
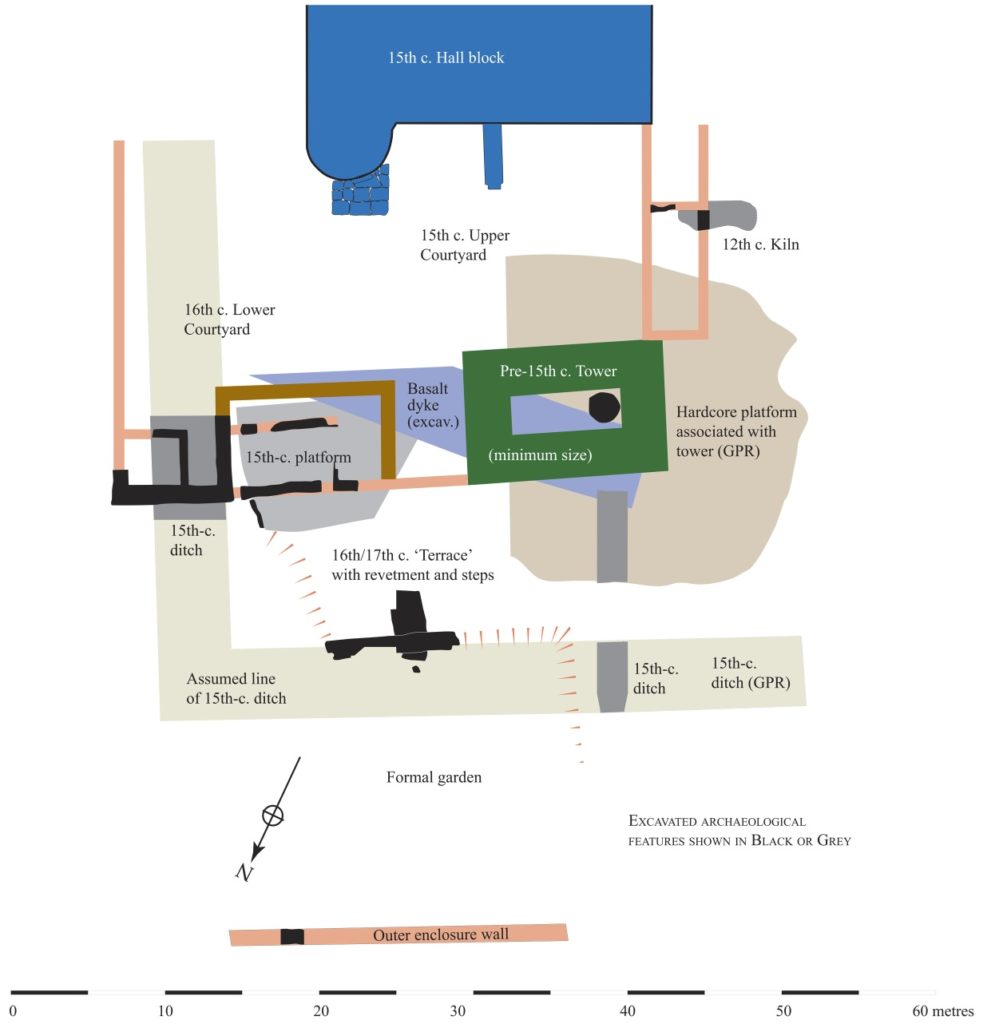
The production of an interpretative phased floor plan for Greasley Castle in Nottinghamshire. The castle, built in the 1340s, has an obscure history and the understanding of its architectural phasing is at best very cloudy. The site is now a working farm and a number of post-mediaeval structures have been conglomerated around the remains of what is suspected to be a fourteenth century courtyard house with projecting corner towers.
The survey will act as baseline research data for a site which has not previously received serious fieldwork or publication and provide a basis for further research but also for any future conservation needs.
Work on the project will start in the early summer when covid restrictions ease.
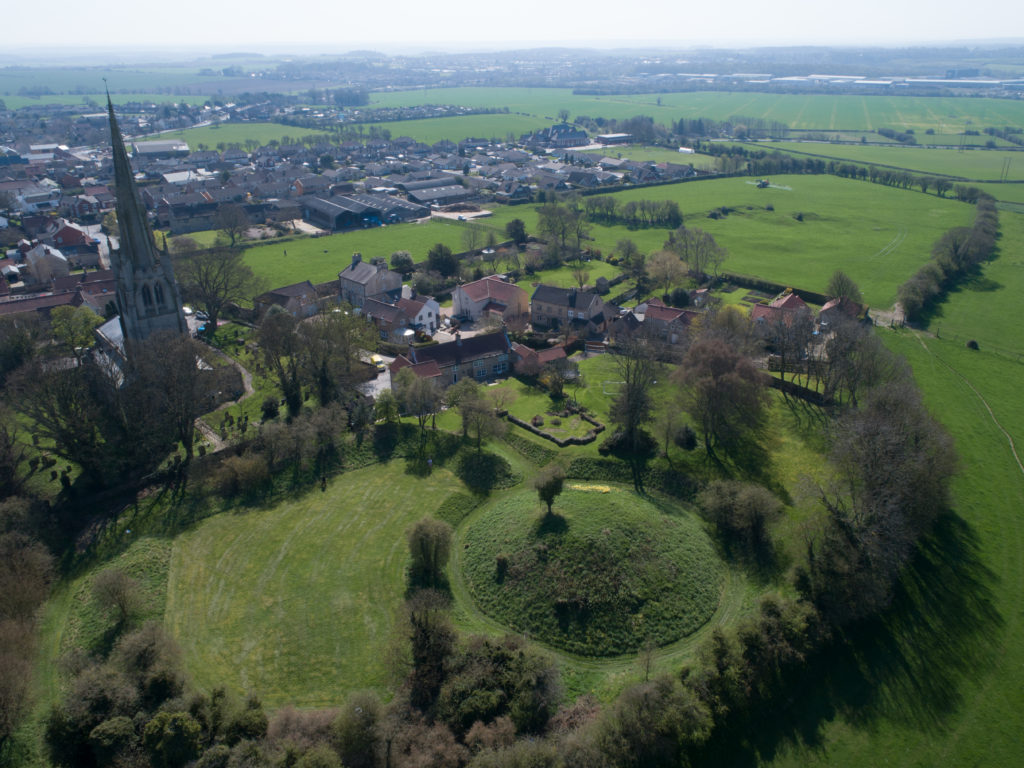

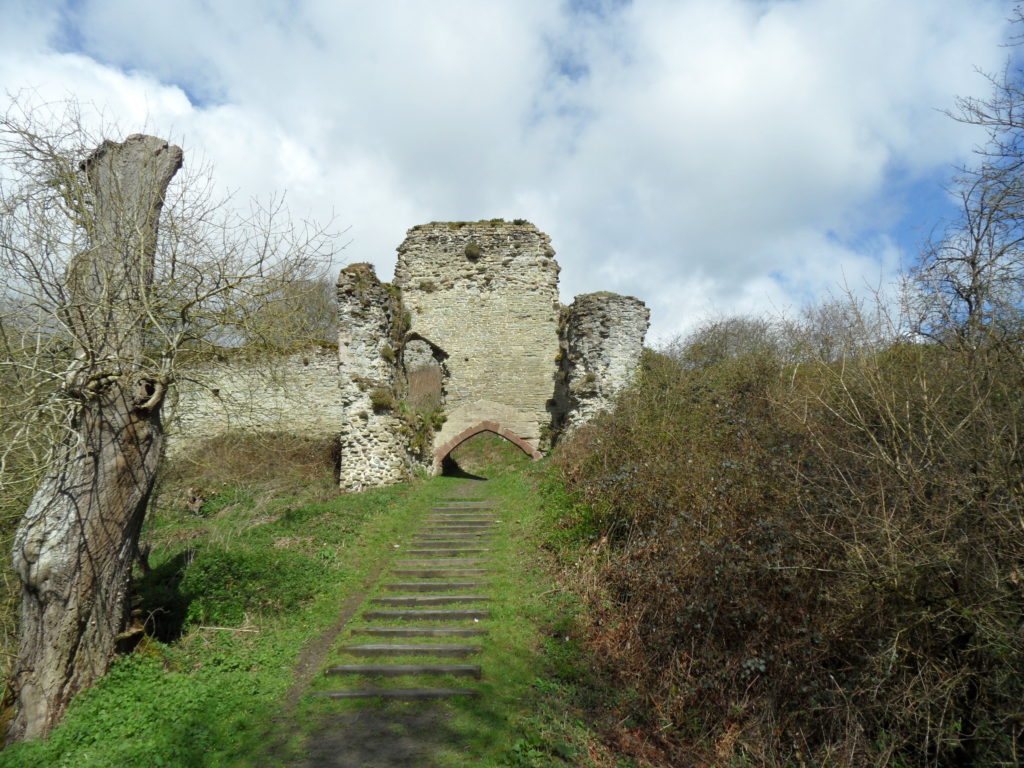
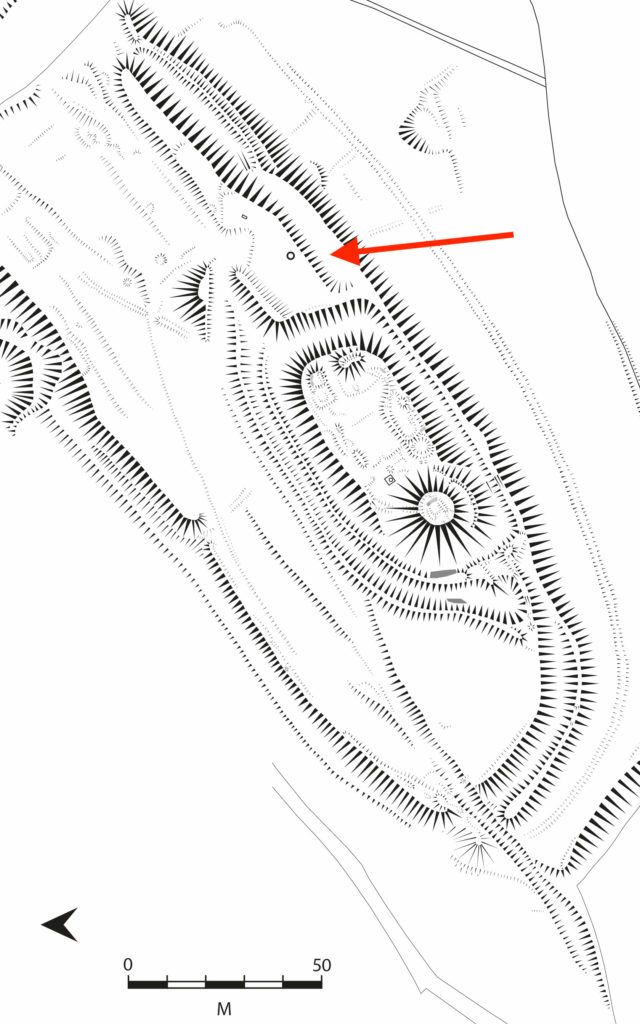
Laughton-en-le-Morthen, South Yorkshire
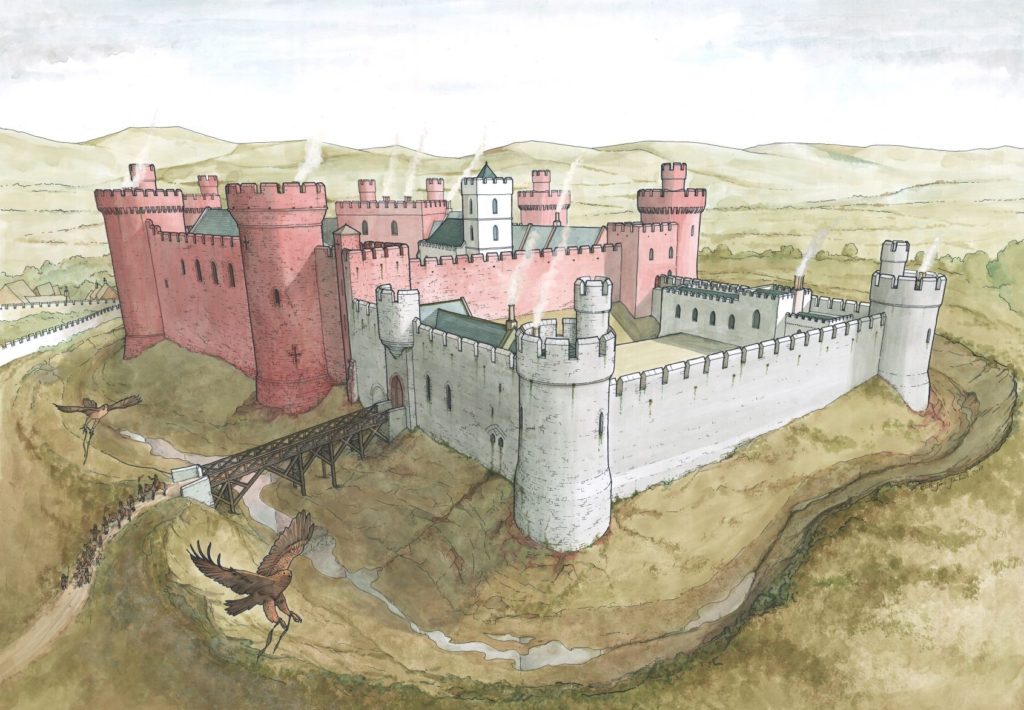
To provide professional illustration and reconstruction which will also be integrated into a co-authored academic article based on the two previous research projects carried out on the site by Dr Duncan Wright and funded by the Trust. A geophysical survey and then small-scale excavation which give a strong indication that the Normans had built a motte on the site of a high-status Saxon dwelling.
Part of the monies will be used to produce phase plans of Laughton during key stages of its development, and a small percentage will pay for a line drawing of the 11th century grave cover incorporated into the fabric of the nearby church. The aim will be to start the work as soon as possible.
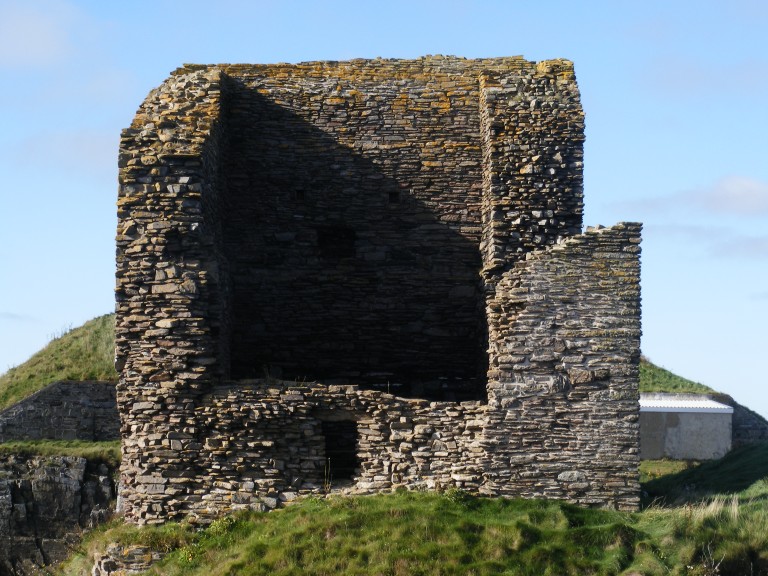

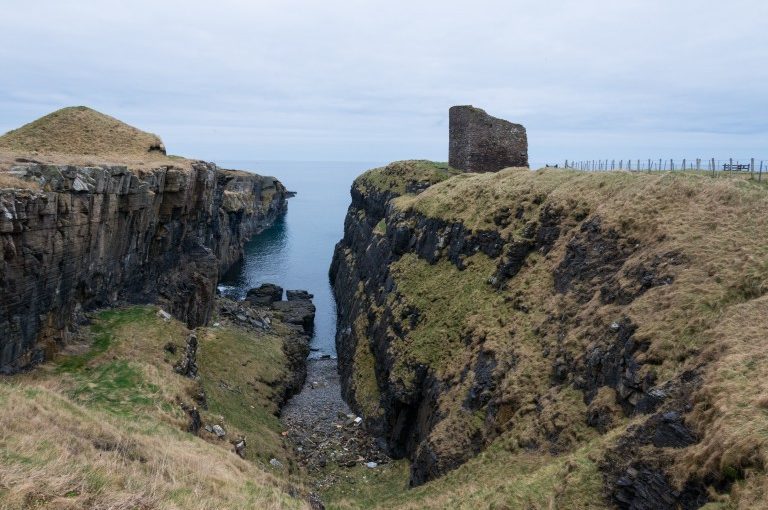
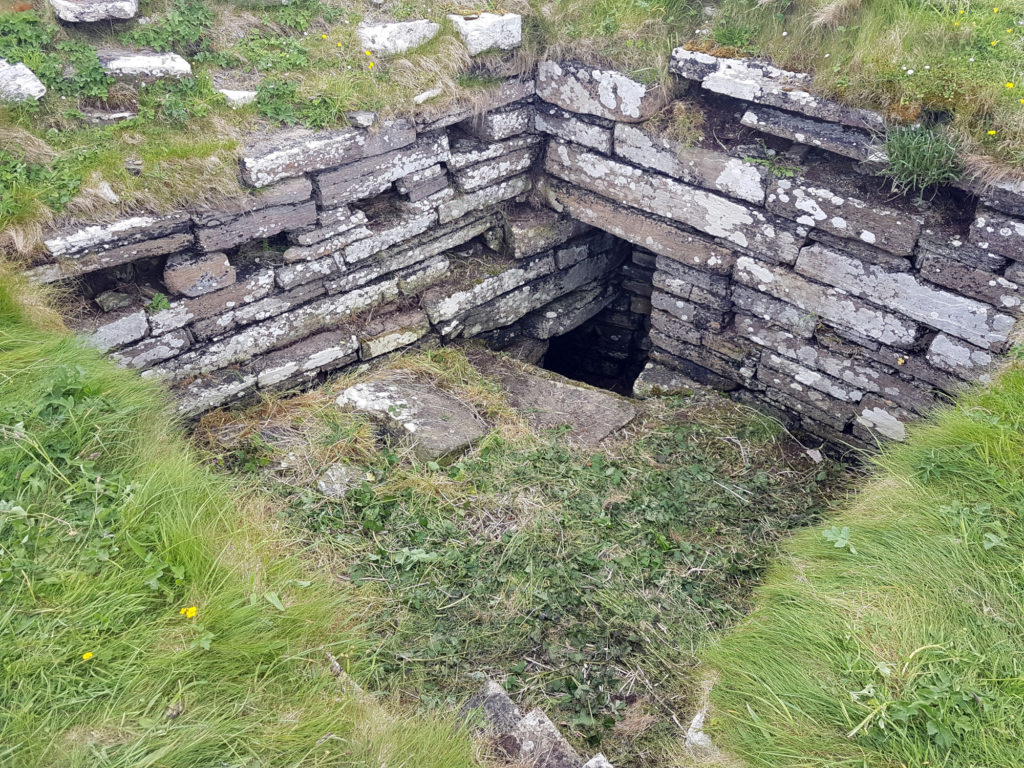
Old Wick, Caithness
Dendrochronological assessment of timber at the Castle of Old Wick, Caithness thought to be one of the earliest stone castles in Scotland dating from the12th century and the period of Scandinavian ascendency. Current thinking though ascribes the date to the 14th century. Analysing these samples will hopefully provide an answer.
With no architectural features or physical “independent” evidence analysing the remains of a timber joist-end (in poor condition) in one of the joist ends remains the best chance of being able to find an answer.
The taking of the samples is likely to take place in September when conditions are still going to be favourable as the castle is situated next to the North Sea and the sample can only be found 8 metres above ground level.
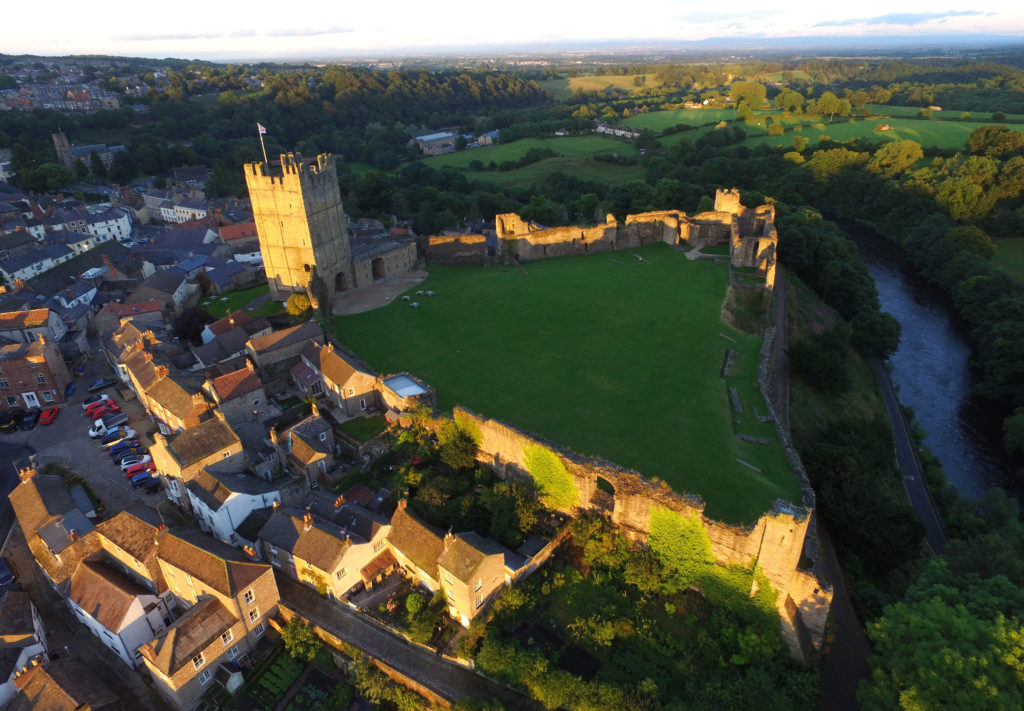

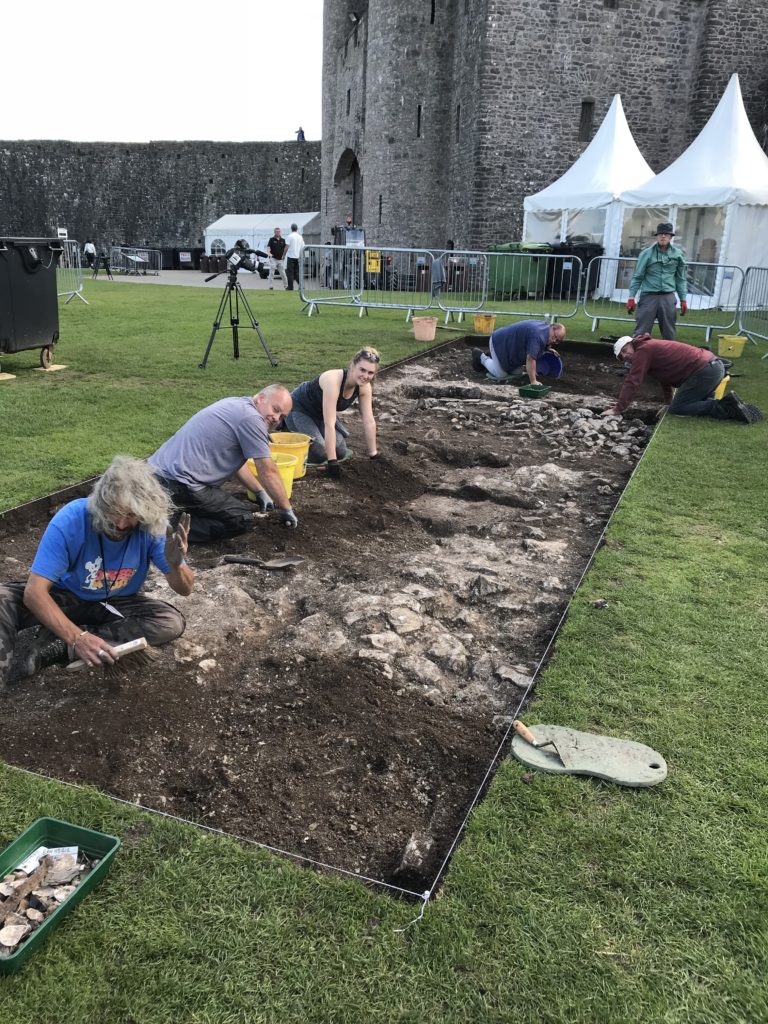
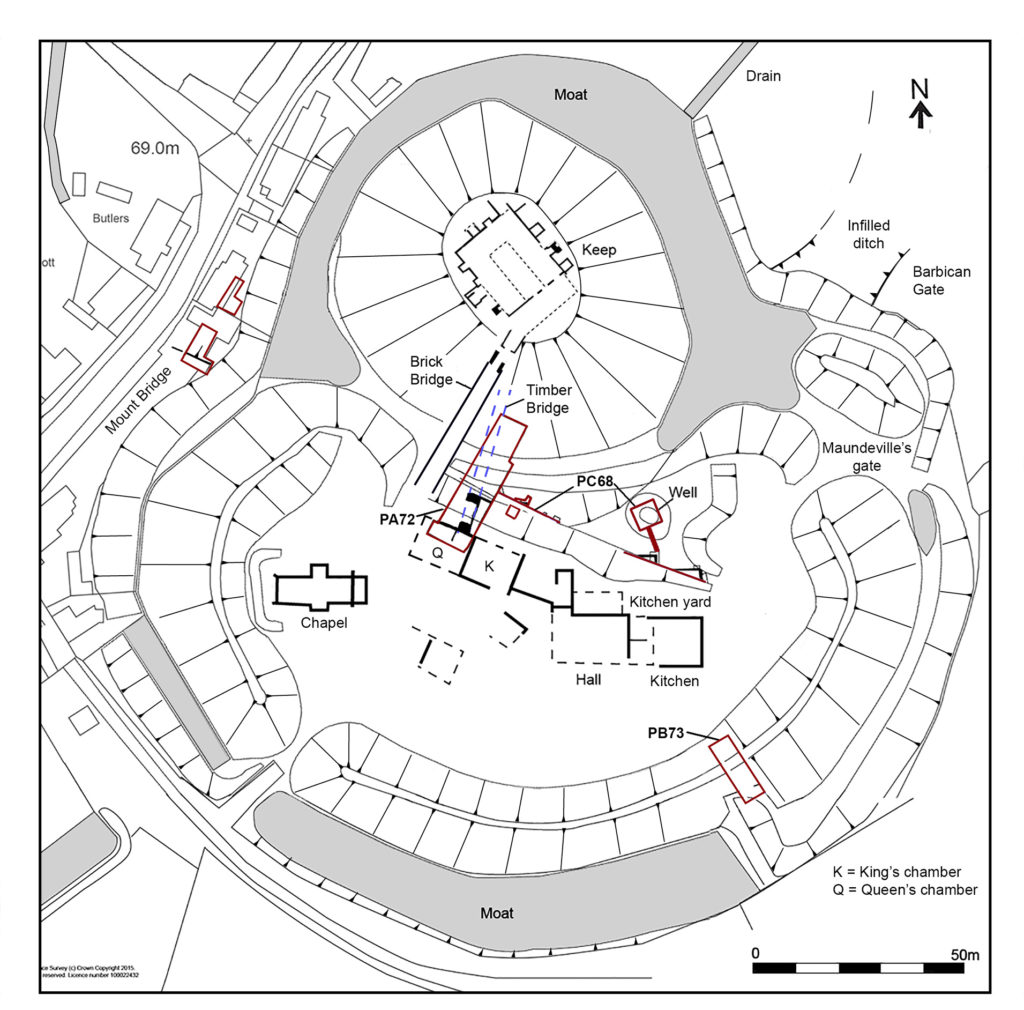
Richmond, North Yorkshire
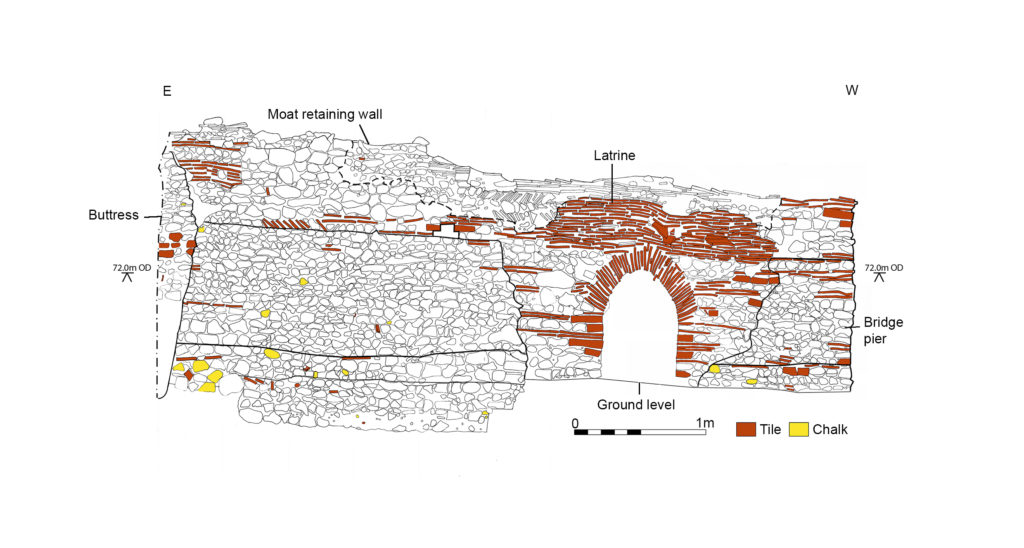
Co-funding a three-week excavation of Richmond Castle, one of the best preserved and least understood Norman castles in the UK. The aim is to understand better the remains of buildings and structures primarily along the eastern side of the bailey including near the 11th century Robin Hood tower and near Scolland’s Hall.
Subject to the scheduled monument consent being granted the excavation will take place in late July.
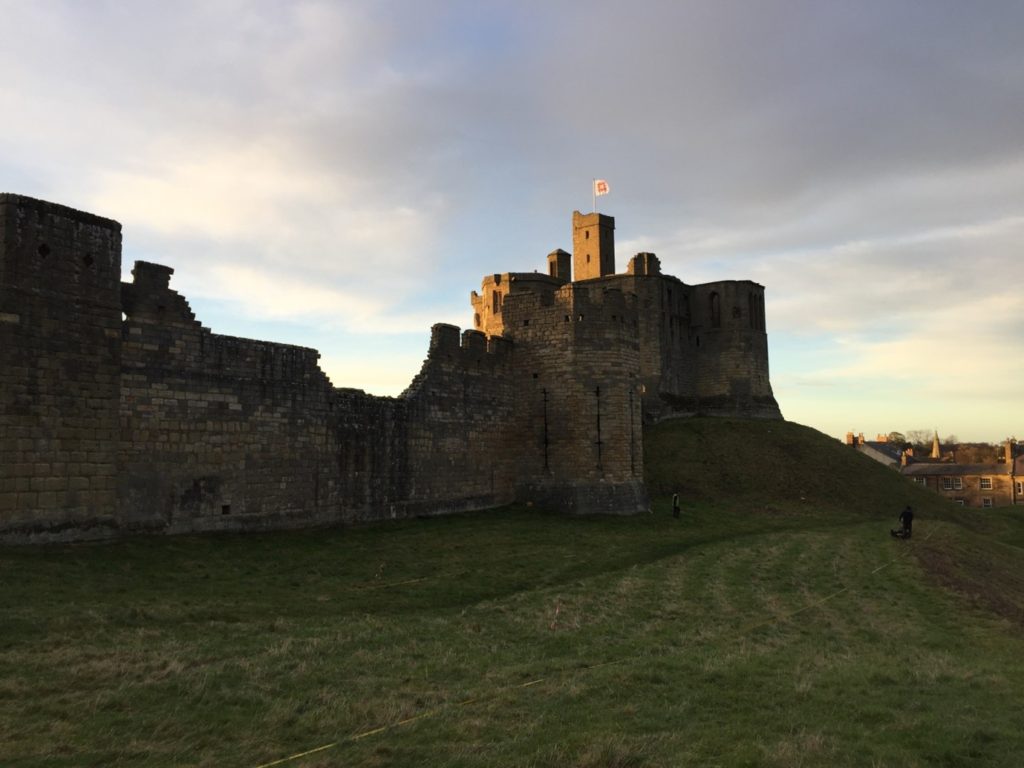

Warkworth, Northumberland
Geophysical survey to explore evidence for subsurface features in and around the field called St John’s Close in a field adjacent to the castle with the aim to establish the location and eastern extent of the castle’s deer park in the 16th century as well as its entrance way. It also hoped to find evidence of a routeway running parallel to the possible park boundary which could represent an early route to the castle’s gatehouse from the south-west.
The plan is to do complete the geophysical survey by the end of March.
To keep up to date with how these projects progress over the coming months you can:
Subscribe to our quarterly newsletter
And if you donate at least £50 here and be invited to our exclusive visits to these projects: https://donate.kindlink.com/castle-studies-trust/2245
Featured image: Old Wick Castle, Caithness, copyright Historic Environment Scotland