In 2016, geophysical survey by Neil Ludlow and Dyfed Archaeological Trust (DAT) revealed the remains of long-vanished buildings, and other features, at Pembroke Castle. This work would not have been possible without the Castle Studies Trust, which funded the entire project.
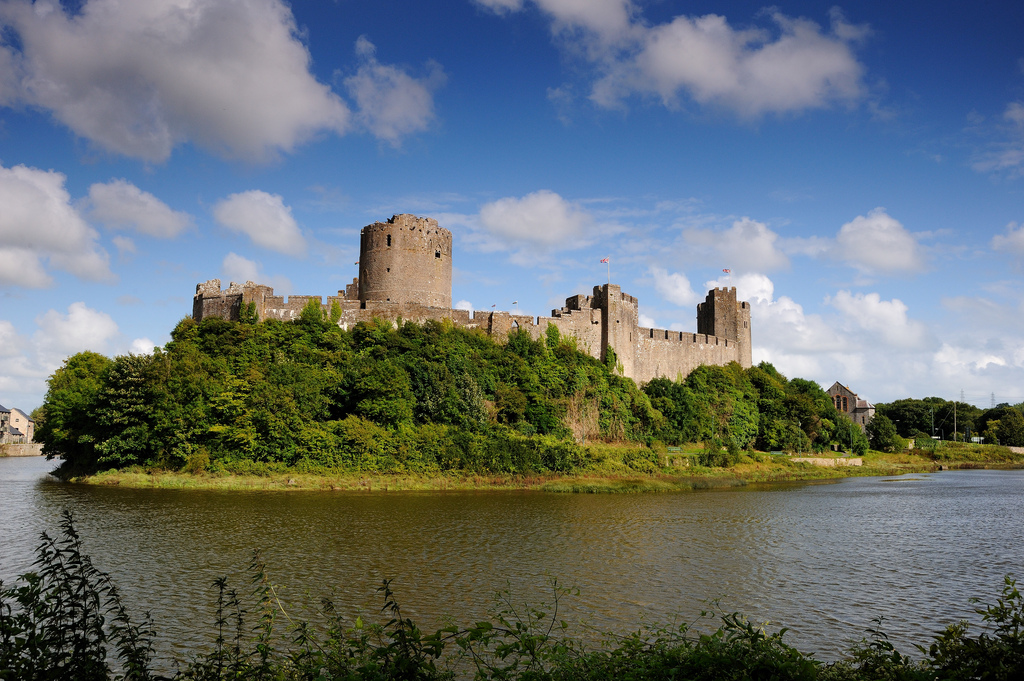
Pembroke is famous for its large round keep, built by earl William Marshal, and a complex of other stone buildings is preserved in the inner ward. But the large, outer ward has been an empty space since at least the eighteenth century. Nevertheless, very dry summers had revealed ‘parchmarks’ here, showing that ruined walls lay just below the surface. These showed up particularly well during 2013 when they were photographed by Toby Driver of the Royal Commission on Ancient and Historical Monuments (Wales), and were published by Toby, with Neil Ludlow, in Archaeology in Wales.
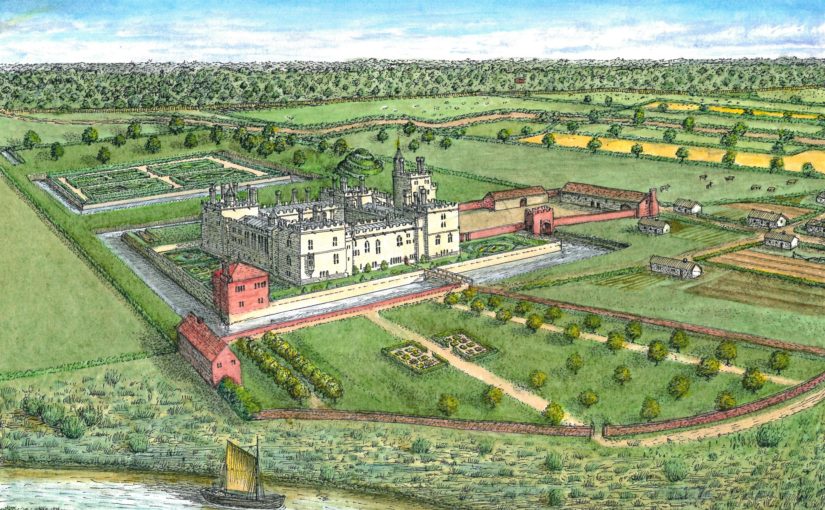
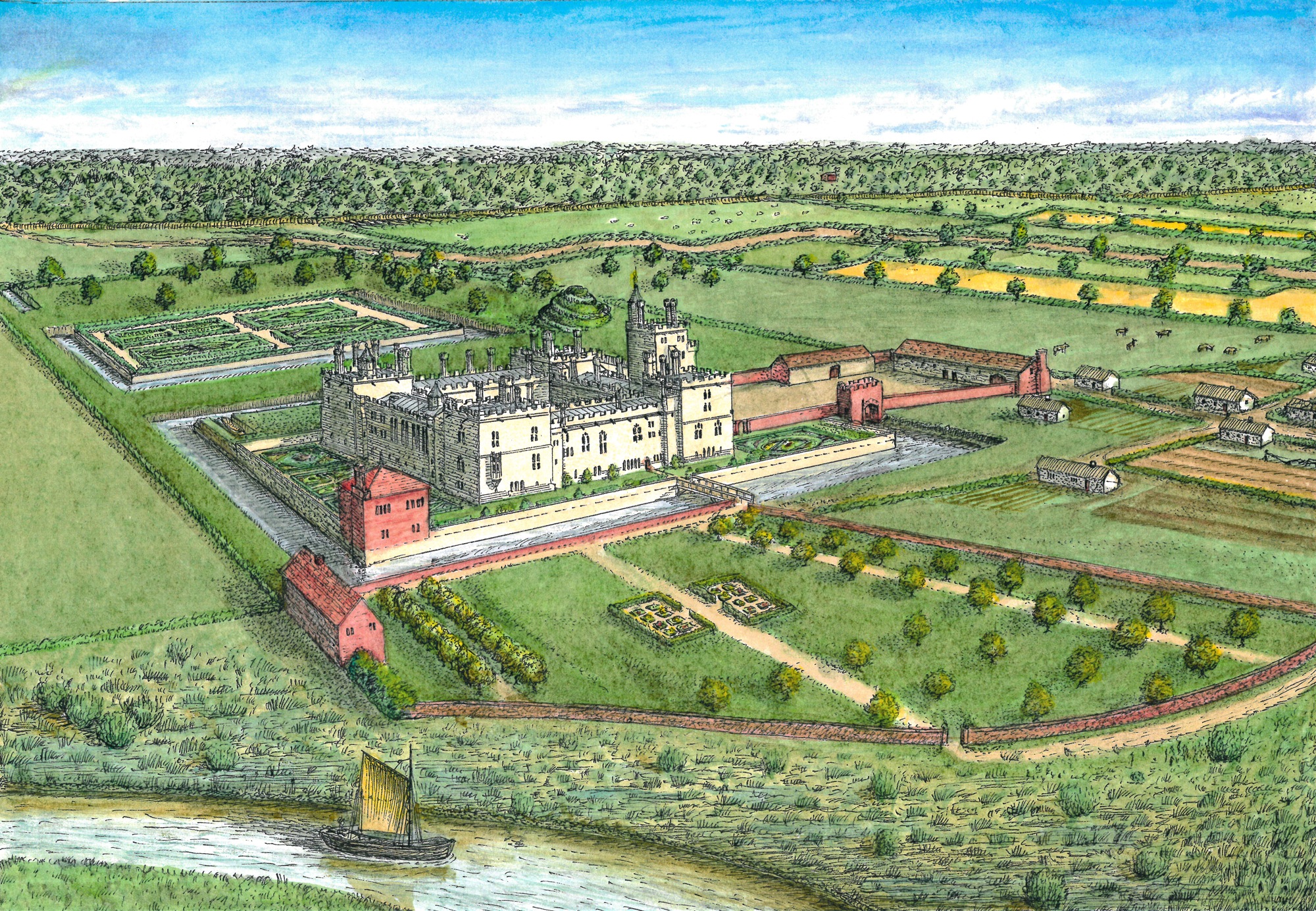
This was the genesis of the current programme of investigation at the castle. The geophysics that followed used a combination of magnetometry, resistivity and Ground Penetrating Radar, to confirm the parchmark evidence and also show that a number of further buildings, and other features, formerly lay in the outer ward. The most exciting of these is a large building which may represent a free-standing, double-winged mansion-house from the late Middle Ages. If so, it would be quite exceptional: grand buildings of this particular kind are unusual in castles, and particularly in outer wards which are normally thought to have contained the more lowly buildings associated with everyday castle life. It means that the outer ward, at Pembroke, may have been ‘gentrified’ – at least in the fifteenth century. This may make sense of historical accounts which place the birth of the future king Henry VII in the outer ward: it may have occurred within this very building.
What the geophysics and parchmarks seem to show is a large, central hall, flanked by two wings. If the building was anything like others of its kind, one wing will have contained the kitchen and ‘services’ – the buttery and pantry – while the other represented more private accommodation. The outer ward was partly excavated in the 1930s – sadly, without record – but a photograph shows a large, stone-lined pit, apparently leading off the hall, which may be the cess-pit mentioned in an account from the period. A square annexe showed up here in the survey work.

While the results showed what can be achieved through geophysics – and generous grant-aid – their interpretation is, at the moment, still speculation. Only educated guesses can be made about the exact form, date and function of the building. But it has the potential to make a big contribution to the study of castles, and late medieval history, at a national level. So Neil got together with James Meek of DAT to decide how best to get answers to these questions. Only excavation could really provide the answers but, given the sensitivity of the site, which is a Scheduled Ancient Monument, and the importance of the building, minimum intervention, for now, was the preferred approach – a small excavation, primarily just to see how much has survived. This was agreed by Cadw, who granted permission for the hand-excavation of two trial trenches, one across the hall and possible cess-pit, the other across one of the wings. Overburden will be removed, and hopefully the remains of the medieval walls, and any floor-surfaces, will be revealed. It is not intended to go down any further – or at least, not in the present project which will effectively be an evaluation.
We also don’t know how much was removed during the 1930s excavation. While we know there must still be walling, as it shows up in the geophysics and parchmarks, it is possible that the medieval floors may have gone. We hope not, and we also hope that the cess-pit wasn’t emptied, as its deposits could contain valuable information on diet, health, bugs and parasites, while finds that are important to us may have been dumped there as rubbish.
Neil and DAT decided once again to approach the Castle Studies Trust who, very generously, again awarded a grant for the work. This will be supported by help in kind from Pembroke Castle Trust. One of the things also missing at Pembroke is a really accurate measured ground plan, with levels, so for the first time a full topographic survey will also be undertaken. We hope the castle can be persuaded to reveal a few more of its secrets.
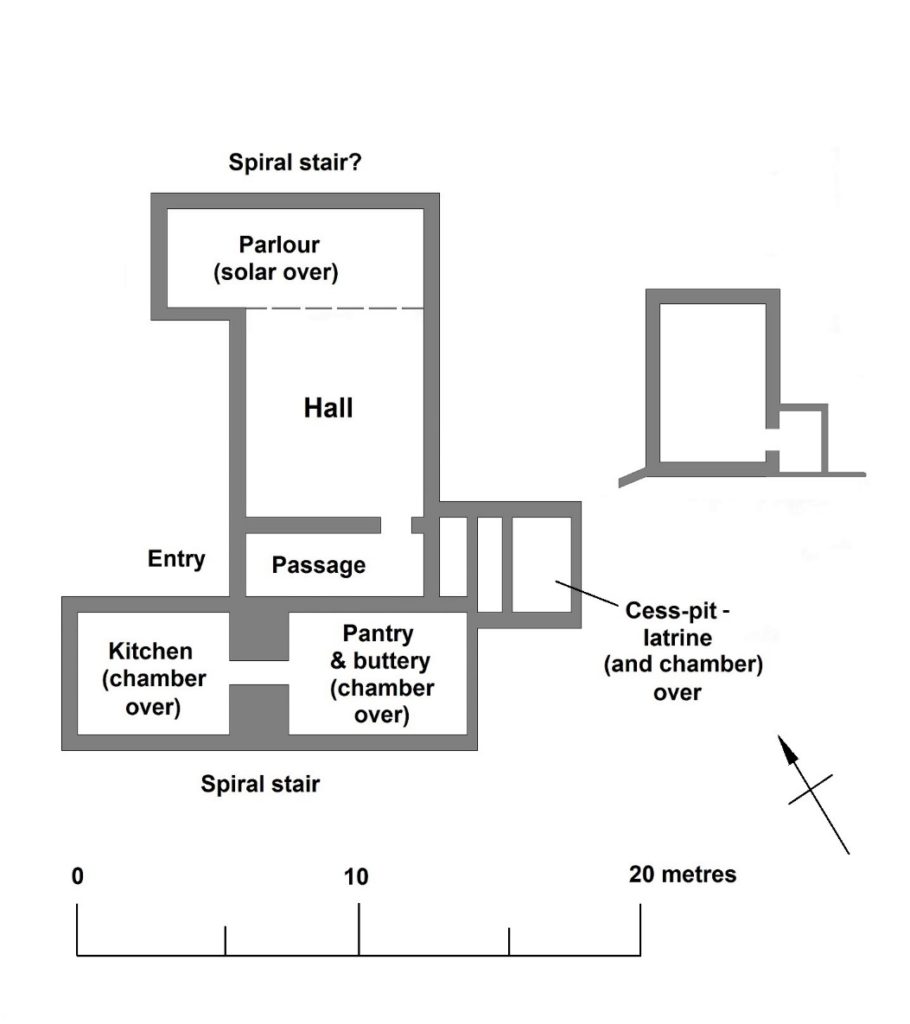
based on Cothay Manor, Somerset, and others. ©Neil Ludlow
Don’t miss out on more news from our projects. We’ll have regular updates from Pembroke on our social media, and if you haven’t already please subscribe to our quarterly newsletter. We are entirely reliant on donations, so please consider giving to support our work.